Duplicate Elimination
Revision as of 11:55, 10 October 2022 by Admin (talk | contribs) (Created page with "== Problem Description== SQL does not eliminate duplicates implicitly. It allows to enter duplicate values on columns other than candidate key or if did not specified any keys. If the user wants to eliminate duplicate records, he has to use DISTINCT keyword in the query. Databases, therefore, can have duplicate entries. The problem deals with identifying and removing duplicates from a database. == Bounds Chart == 1050px ==...")
Problem Description
SQL does not eliminate duplicates implicitly. It allows to enter duplicate values on columns other than candidate key or if did not specified any keys. If the user wants to eliminate duplicate records, he has to use DISTINCT keyword in the query.
Databases, therefore, can have duplicate entries. The problem deals with identifying and removing duplicates from a database.
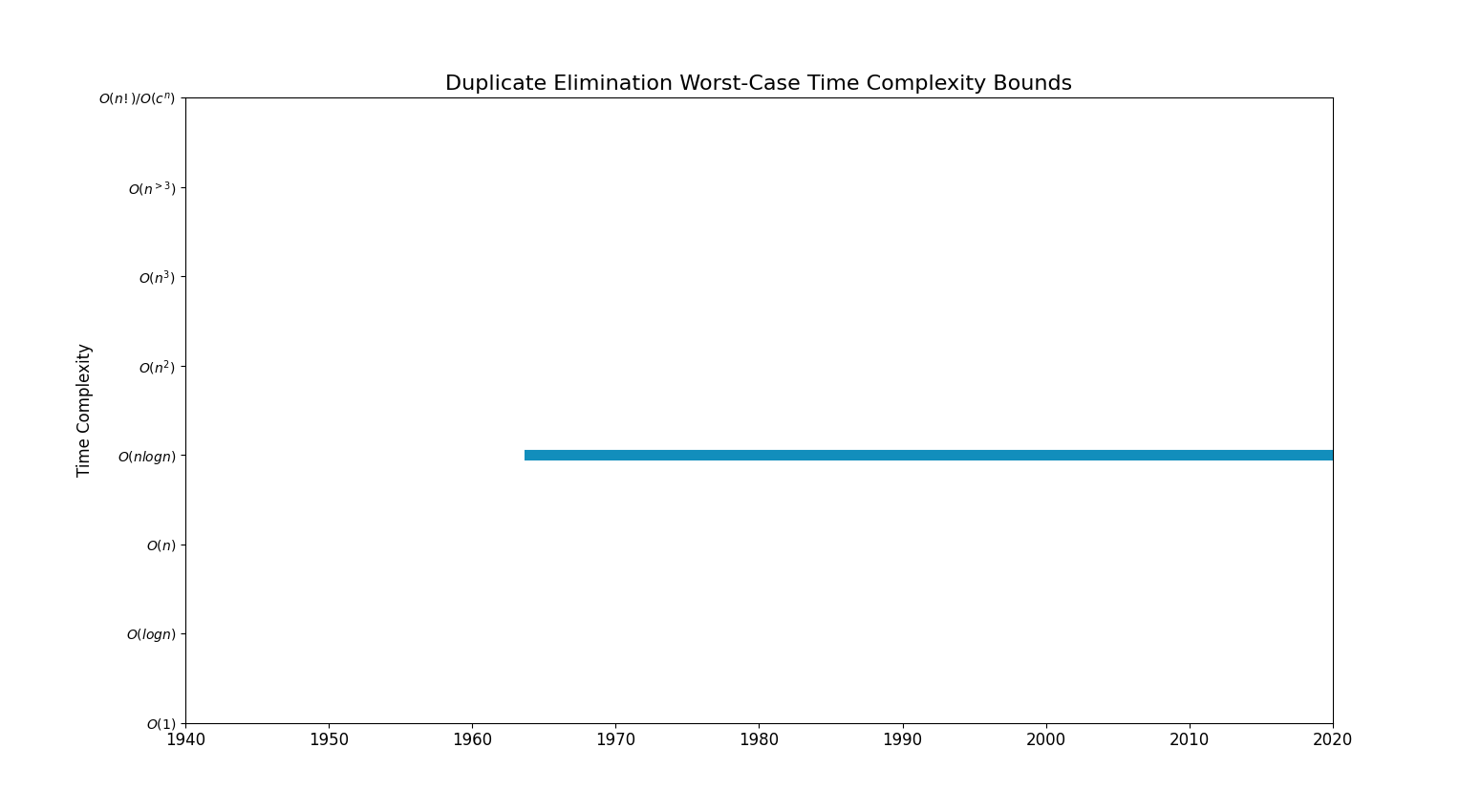
Bounds Chart
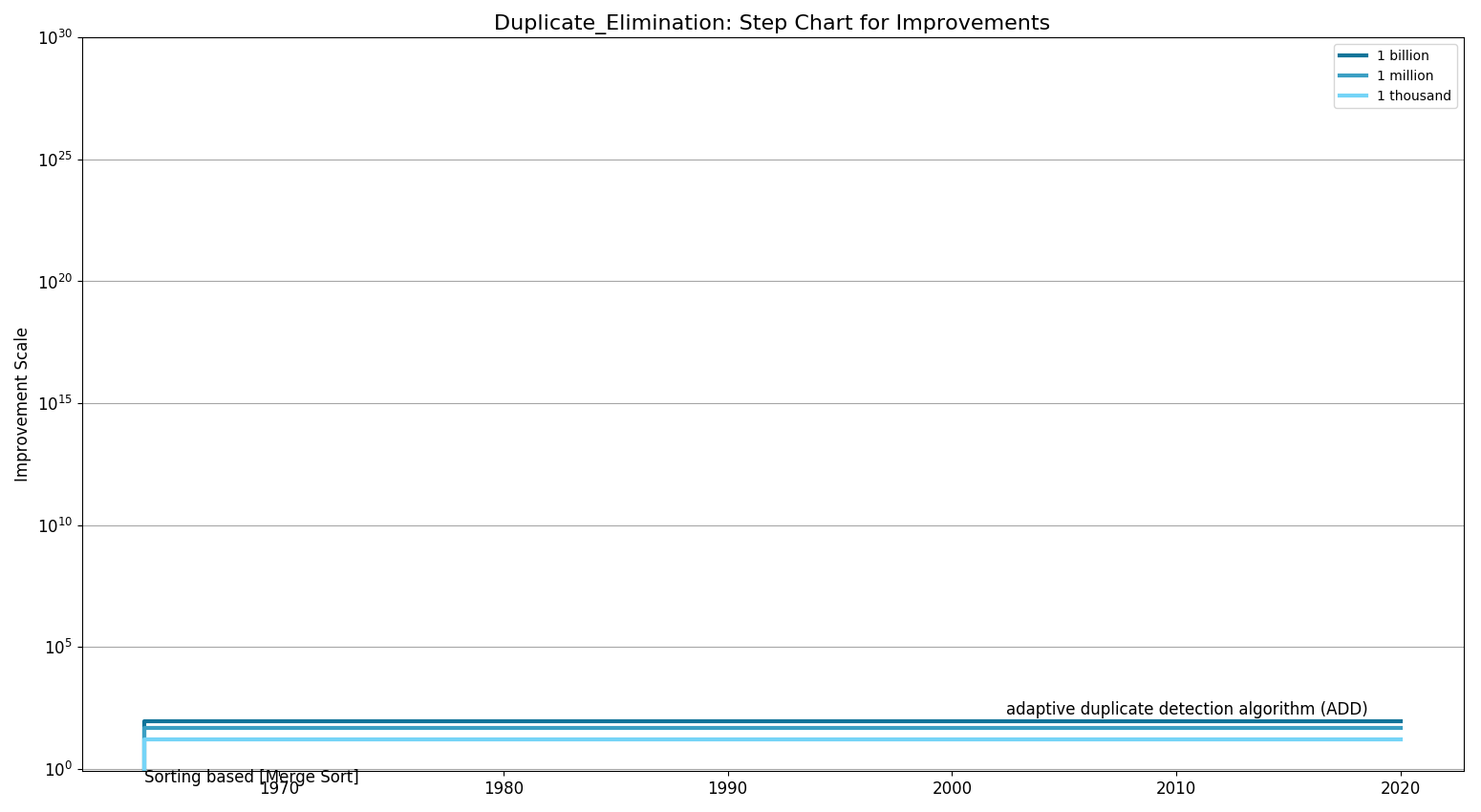
Step Chart
Improvement Table
| Complexity Classes | Algorithm Paper Links | Lower Bounds Paper Links |
|---|---|---|
| Exp/Factorial | ||
| Polynomial > 3 | ||
| Cubic | ||
| Quadratic | [ Priority Queue Algorithm (1976)] | |
| nlogn | [Sorting based [Merge Sort] (1964)]
[Sorting based [Merge Sort] + real-time elimination (1964)] [BST Algorithm (1999)] [sorted neighborhood algorithm (1993)] [Duplicate elimination sorted neighborhood algorithm (DE-SNA) (2002)] |
|
| Linear | ||
| logn |