Discrete Fourier Transform
Revision as of 11:55, 10 October 2022 by Admin (talk | contribs) (Created page with "== Problem Description== In mathematics, the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) converts a finite sequence of equally-spaced samples of a function into a same-length sequence of equally-spaced samples of the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT), which is a complex-valued function of frequency. == Bounds Chart == 350px == Step Chart == 350px == Improvement Table == {| cl...")
Problem Description
In mathematics, the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) converts a finite sequence of equally-spaced samples of a function into a same-length sequence of equally-spaced samples of the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT), which is a complex-valued function of frequency.
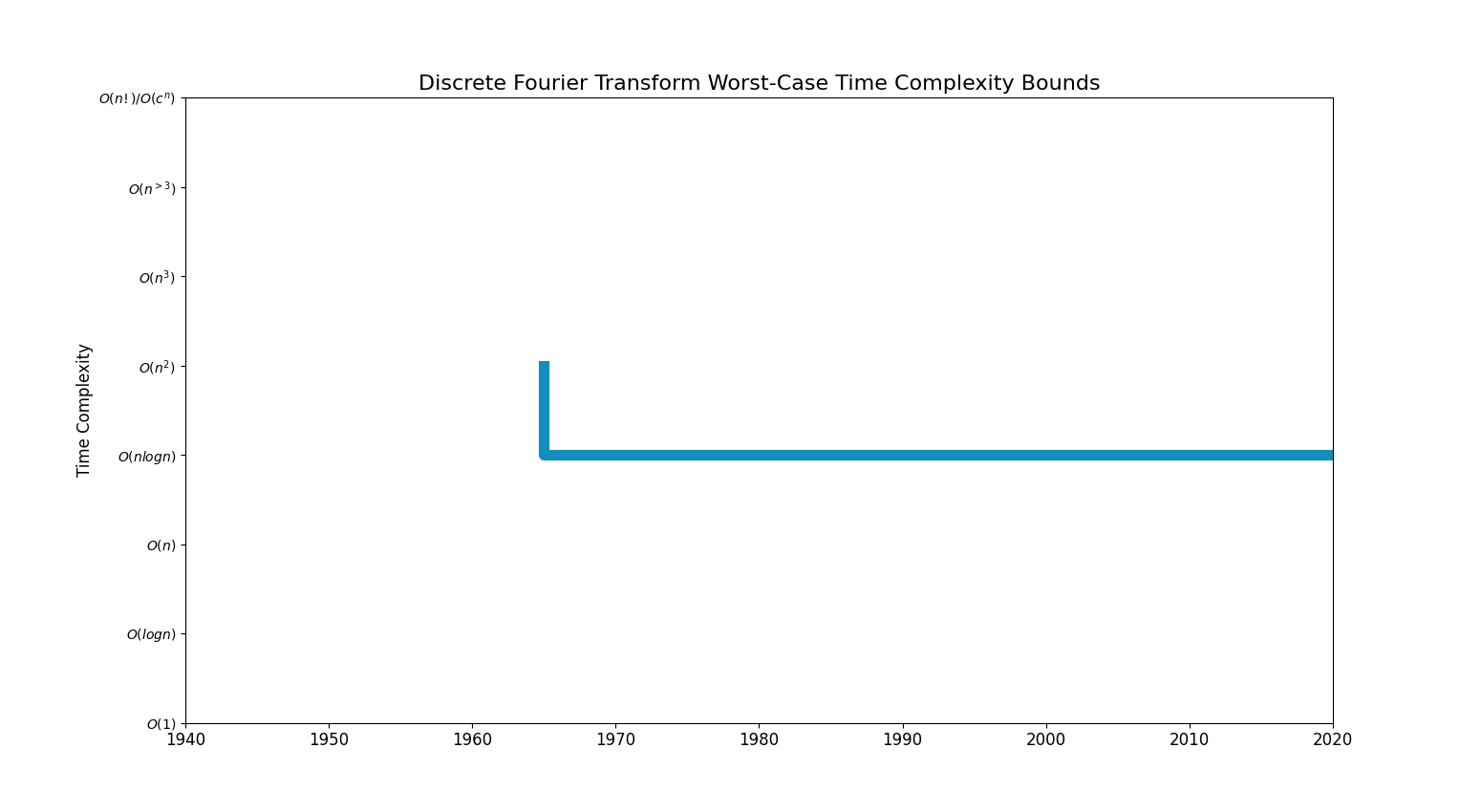
Bounds Chart
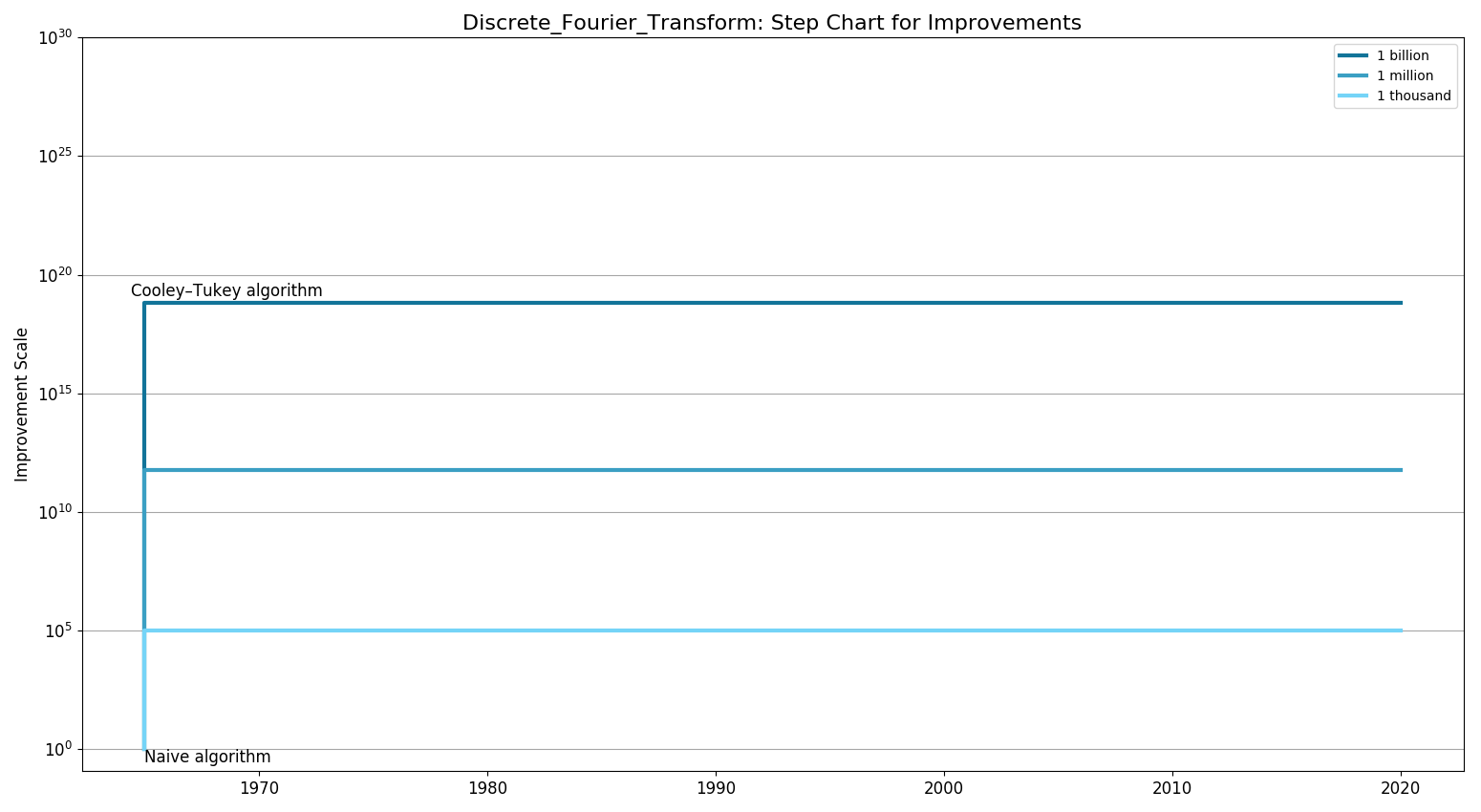
Step Chart
Improvement Table
| Complexity Classes | Algorithm Paper Links | Lower Bounds Paper Links |
|---|---|---|
| Exp/Factorial | ||
| Polynomial > 3 | ||
| Cubic | ||
| Quadratic | ||
| nlogn | ||
| Linear | ||
| logn |