All-pairs shortest paths (Undirected)
Revision as of 11:54, 10 October 2022 by Admin (talk | contribs) (Created page with "== Problem Description== It aims to figure out the shortest path from each vertex v to every other u. Storing all the paths explicitly can be very memory expensive indeed, as we need one spanning tree for each vertex. This is often impractical regarding memory consumption, so these are generally considered as all pairs-shortest distance problems, which aim to find just the distance from each to each node to another. We usually want the output in tabular form: the entry i...")
Problem Description
It aims to figure out the shortest path from each vertex v to every other u. Storing all the paths explicitly can be very memory expensive indeed, as we need one spanning tree for each vertex. This is often impractical regarding memory consumption, so these are generally considered as all pairs-shortest distance problems, which aim to find just the distance from each to each node to another. We usually want the output in tabular form: the entry in u's row and v's column should be the weight of the shortest path from u to v.
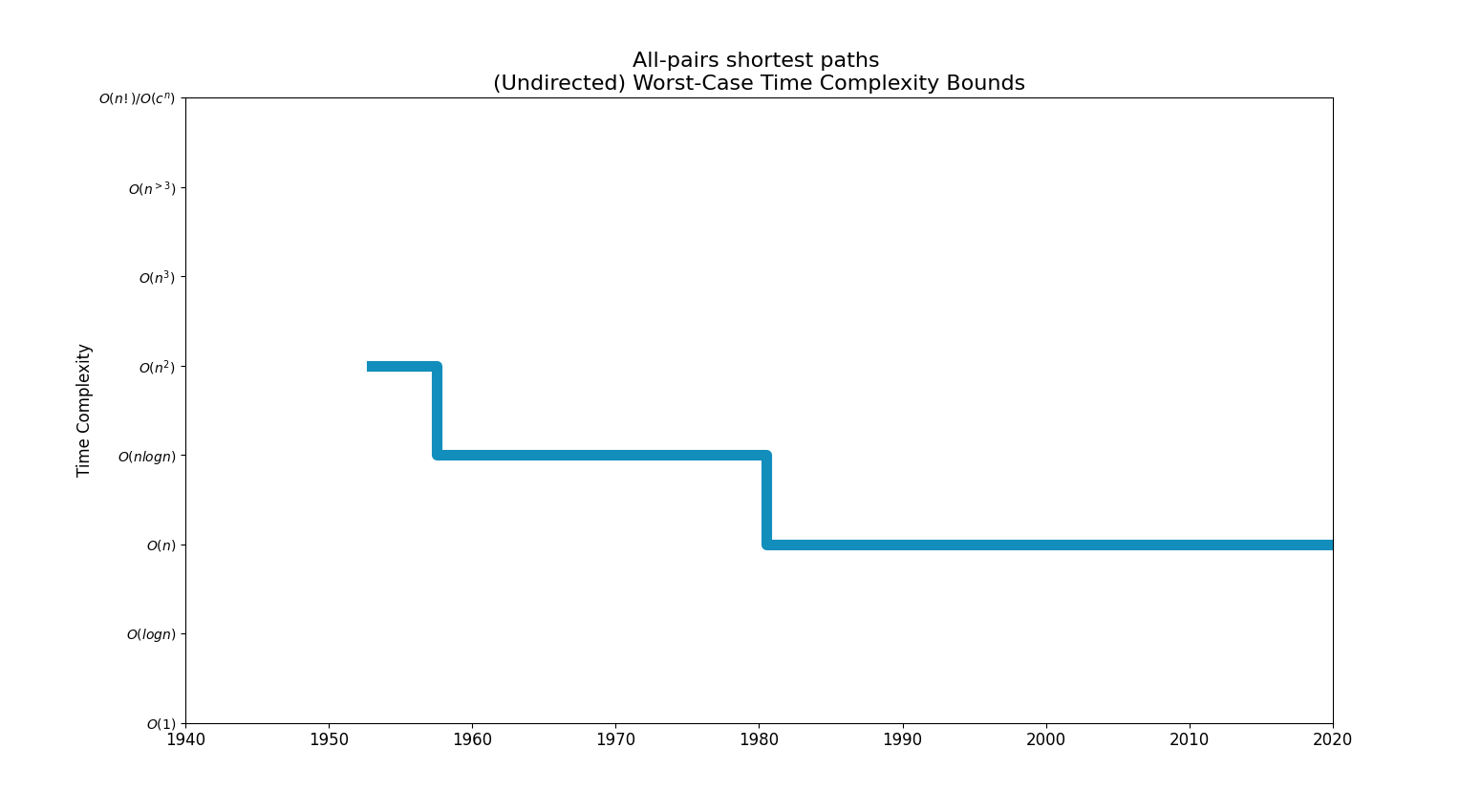
Bounds Chart
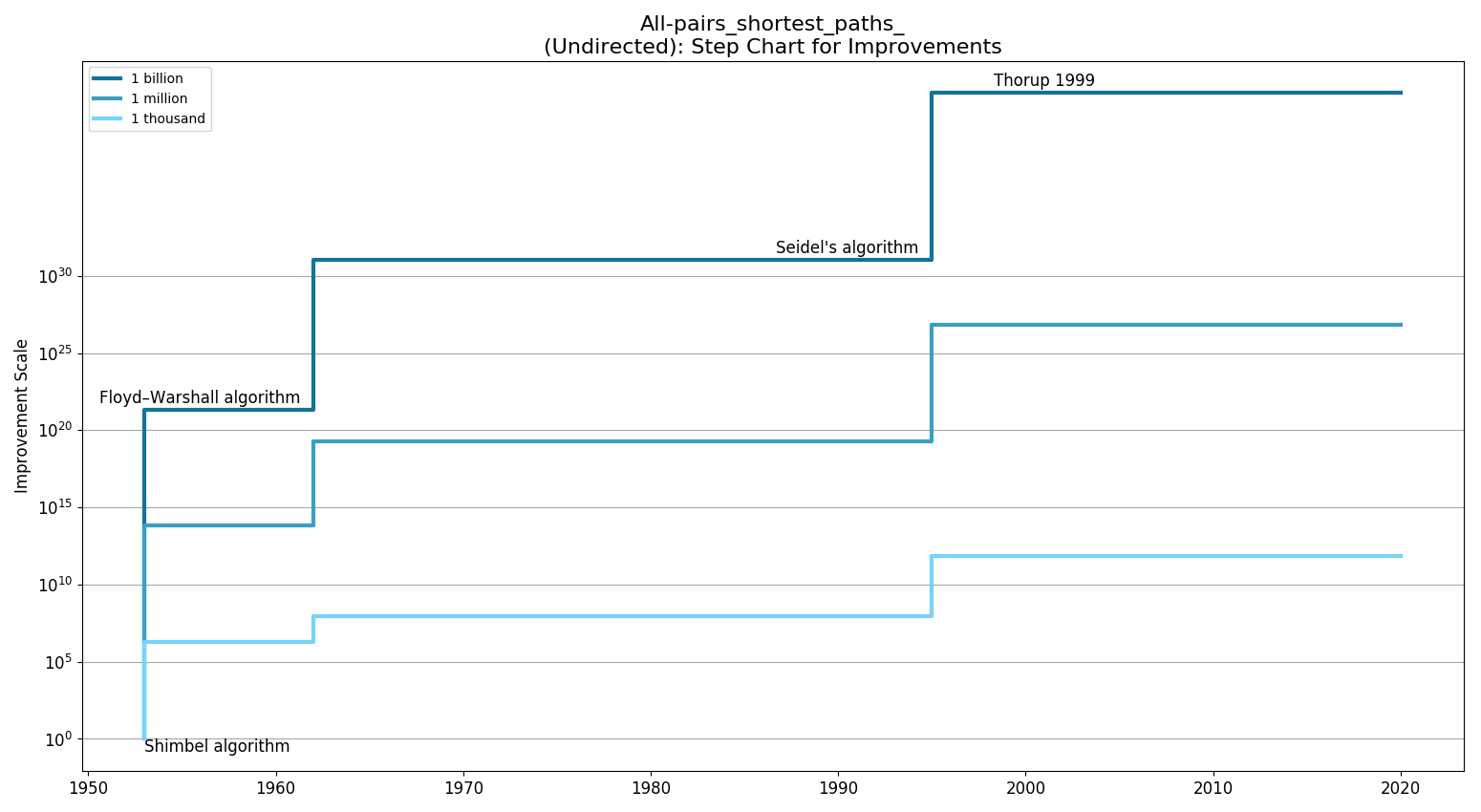
Step Chart
Improvement Table
| Complexity Classes | Algorithm Paper Links | Lower Bounds Paper Links |
|---|---|---|
| Exp/Factorial | ||
| Polynomial > 3 | Shimbel algorithm (1953) | |
| Cubic | Floyd–Warshall algorithm (1962) | |
| Quadratic | Thorup 1999 (1999) | |
| nlogn | ||
| Linear | ||
| logn |