Shortest Path(Directed graphs)
Revision as of 11:00, 10 October 2022 by Admin (talk | contribs) (Created page with "== Problem Description== The shortest path problem involves finding the shortest path between two vertices (or nodes) in a graph. Algorithms such as the Floyd-Warshall algorithm and different variations of Dijkstra's algorithm are used to find solutions to the shortest path problem. Applications of the shortest path problem include those in road networks, logistics, communications, electronic design, power grid contingency analysis, and community detection. == Bounds...")
Problem Description
The shortest path problem involves finding the shortest path between two vertices (or nodes) in a graph. Algorithms such as the Floyd-Warshall algorithm and different variations of Dijkstra's algorithm are used to find solutions to the shortest path problem.
Applications of the shortest path problem include those in road networks, logistics, communications, electronic design, power grid contingency analysis, and community detection.
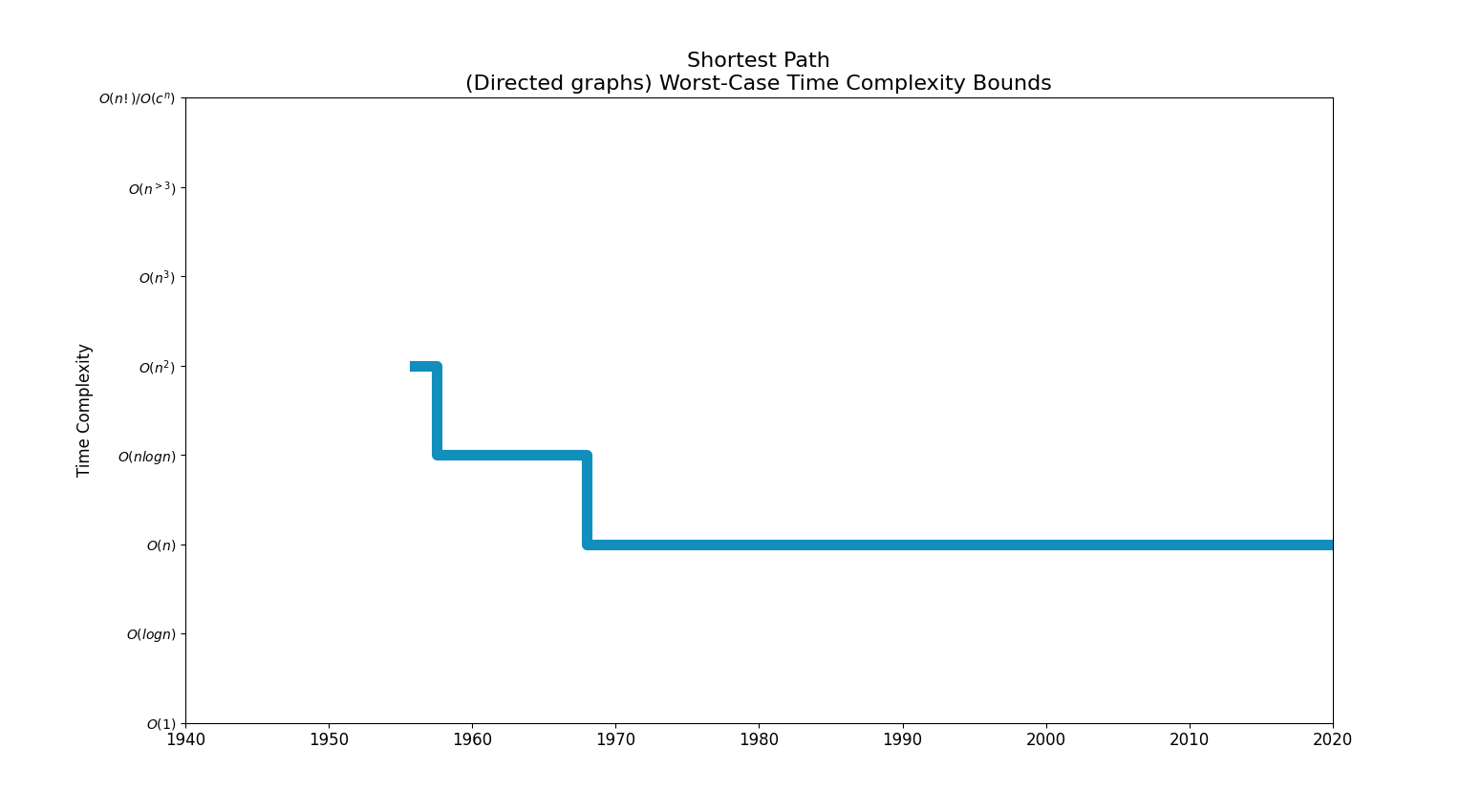
Bounds Chart
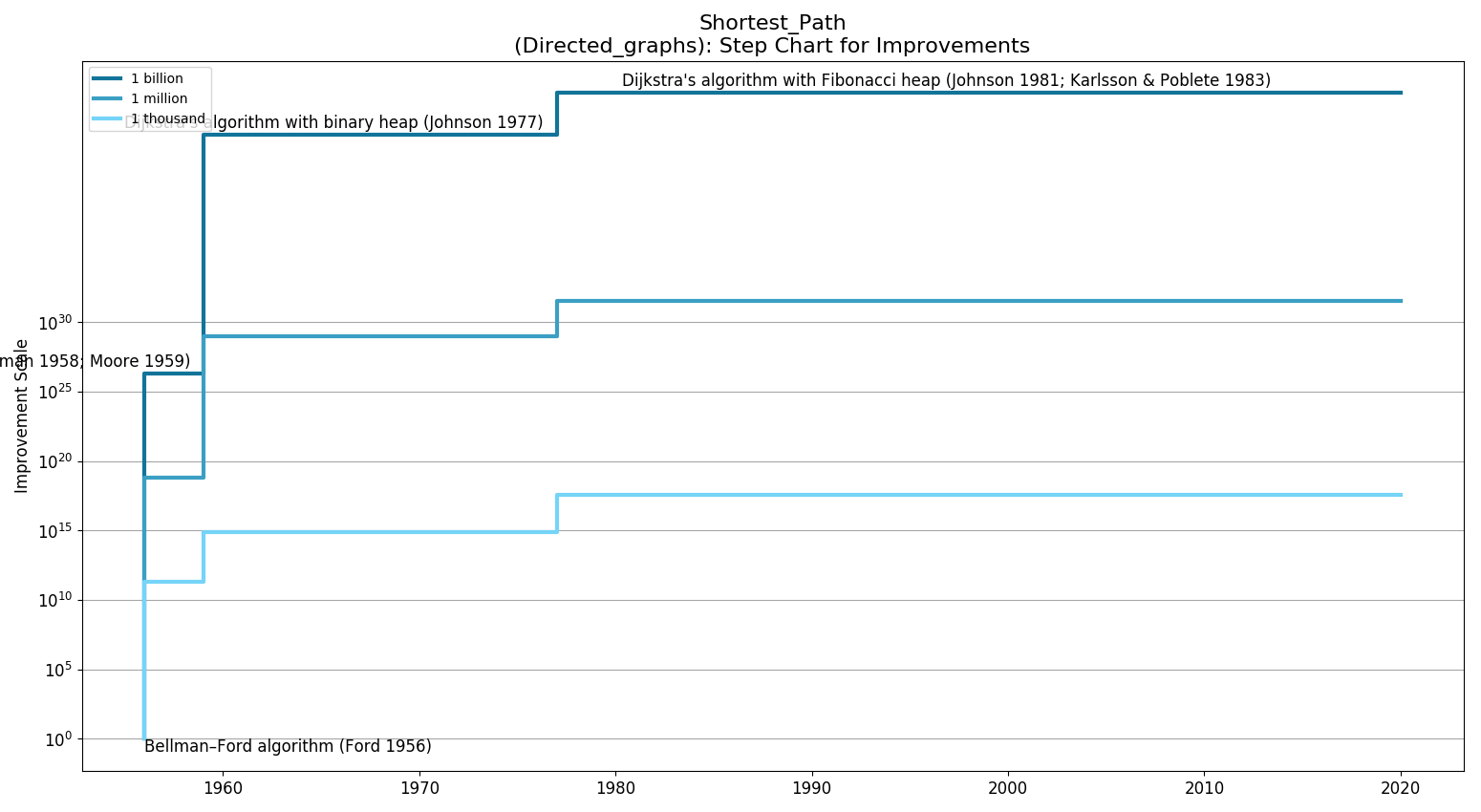
Step Chart
Improvement Table
| Complexity Classes | Algorithm Paper Links | Lower Bounds Paper Links |
|---|---|---|
| Exp/Factorial | ||
| Polynomial > 3 | ||
| Cubic | Bellman–Ford algorithm (Ford 1956) (1956) | |
| Quadratic | Bellman–Ford algorithm (Shimbel 1955; Bellman 1958; Moore 1959) (1959)
Dijkstra's algorithm with list (Whiting & Hillier 1960) (1960) Dijkstra's algorithm with binary heap (Johnson 1977) (1977) Dijkstra's algorithm with Fibonacci heap (Fredman & Tarjan 1984; Fredman & Tarjan 1987) (1984) |
|
| nlogn | Dijkstra's algorithm with Fibonacci heap (Johnson 1981; Karlsson & Poblete 1983) (1981) | |
| Linear | [ Gabow's algorithm (1983)]
[ Gabow Ahuja algorithm (1990)] |
|
| logn |