NFA to DFA conversion
Revision as of 11:59, 10 October 2022 by Admin (talk | contribs) (Created page with "== Problem Description== DFA refers to Deterministic Finite Automaton. A Finite Automata(FA) is said to be deterministic, if corresponding to an input symbol, there is single resultant state i.e. there is only one transition. NFA refers to Nondeterministic Finite Automaton. A Finite Automata(FA) is said to be non deterministic, if there is more than one possible transition from one state on the same input symbol. == Bounds Chart == File:NFA_to_DFA_conversionBoundsC...")
Problem Description
DFA refers to Deterministic Finite Automaton. A Finite Automata(FA) is said to be deterministic, if corresponding to an input symbol, there is single resultant state i.e. there is only one transition.
NFA refers to Nondeterministic Finite Automaton. A Finite Automata(FA) is said to be non deterministic, if there is more than one possible transition from one state on the same input symbol.
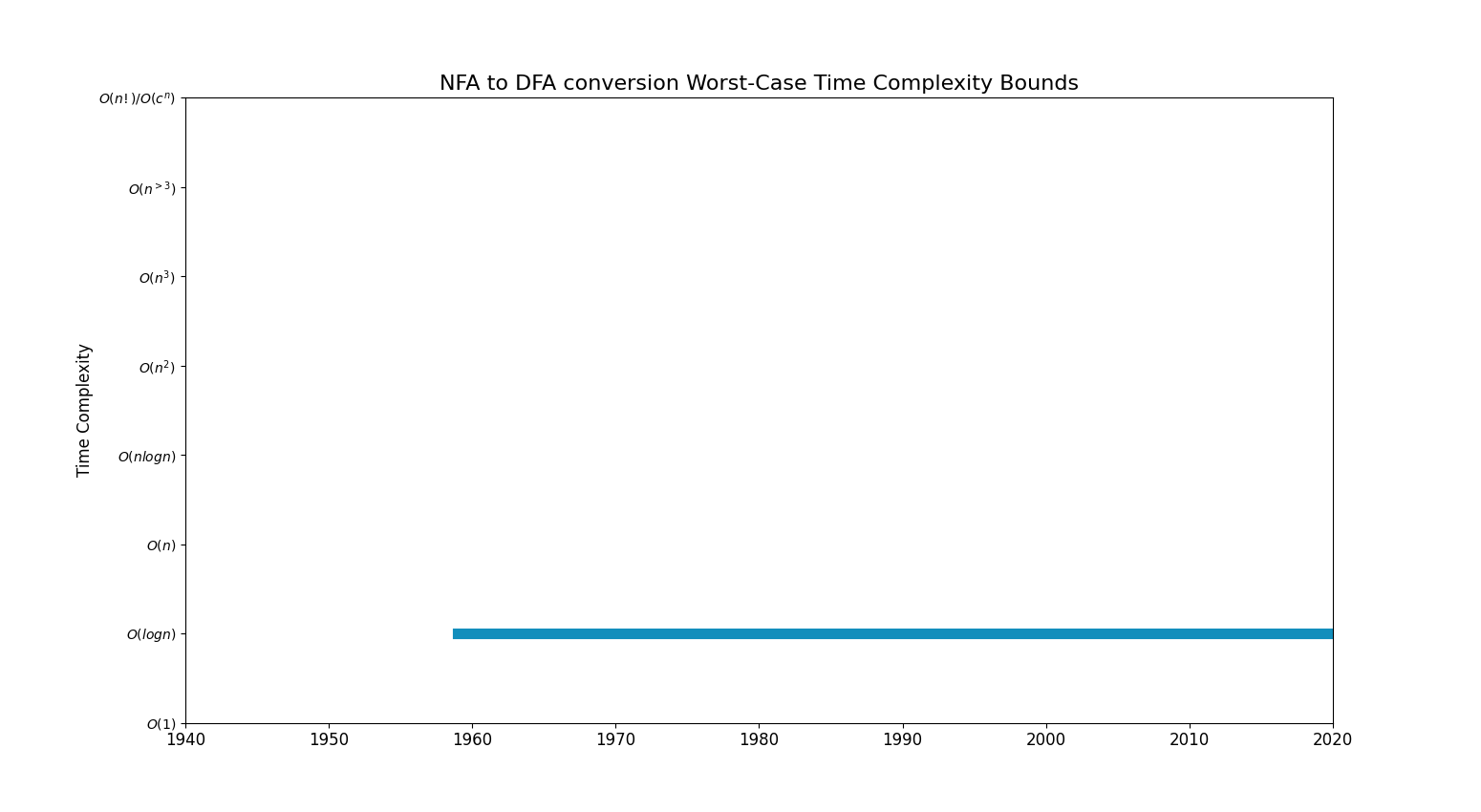
Bounds Chart
Step Chart
Improvement Table
| Complexity Classes | Algorithm Paper Links | Lower Bounds Paper Links |
|---|---|---|
| Exp/Factorial | Rabin–Scott powerset construction (1959) | |
| Polynomial > 3 | ||
| Cubic | ||
| Quadratic | ||
| nlogn | ||
| Linear | ||
| logn |