De Novo Genome Assembly: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
[[File:De Novo Genome Assembly - Time.png|1000px]] | [[File:De Novo Genome Assembly - Time.png|1000px]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:09, 28 April 2023
Description
De novo sequencing refers to sequencing a novel genome where there is no reference sequence available for alignment. Sequence reads are assembled as contigs, and the coverage quality of de novo sequence data depends on the size and continuity of the contigs (ie, the number of gaps in the data).
Parameters
$n$: sum of lengths of reads
$f$: number of input sequences
Table of Algorithms
| Name | Year | Time | Space | Approximation Factor | Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overlap Layout Consensus | 1987 | $O(n^{2})$ | $O(n^{2})$? | Deterministic | ||
| Greedy SEQAID | 1984 | $O(n^{2})$? | $O(n^{2})$? | Deterministic | Time | |
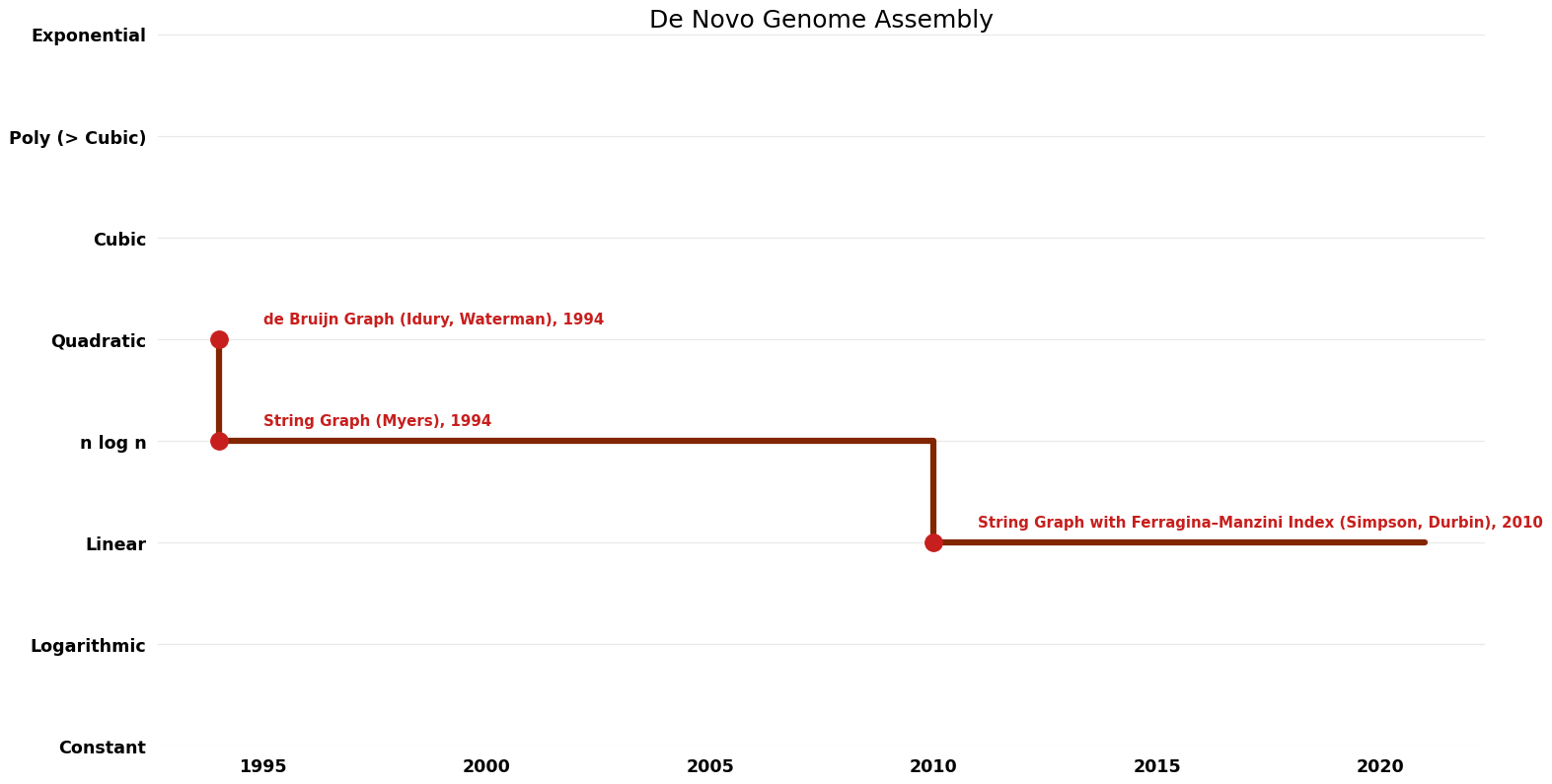
| de Bruijn Graph (Idury, Waterman) | 1994 | $O(n^{2})$ | $O(n)$? | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| String Graph (Myers) | 1994 | $O(n \log n)$ | $O(n)$? | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| String Graph with Ferragina–Manzini Index (Simpson, Durbin) | 2010 | $O(n)$ | $O(n)$? | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Hybrid Algorithm | 1999 | $O(n^{2})$ | Exact | Deterministic |