Bipartite Maximum-Weight Matching: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
[[File:Maximum-Weight Matching - Bipartite Maximum-Weight Matching - Space.png|1000px]] | [[File:Maximum-Weight Matching - Bipartite Maximum-Weight Matching - Space.png|1000px]] | ||
== Space | == Time-Space Tradeoff == | ||
[[File:Maximum-Weight Matching - Bipartite Maximum-Weight Matching - Pareto Frontier.png|1000px]] | [[File:Maximum-Weight Matching - Bipartite Maximum-Weight Matching - Pareto Frontier.png|1000px]] | ||
Revision as of 15:44, 15 February 2023
Description
In computer science, the maximum weight matching problem is the problem of finding, in a weighted graph, a matching in which the sum of weights is maximized. Here, the graph must be bipartite.
Related Problems
Generalizations: Maximum-Weight Matching
Parameters
n: number of vertices
m: number of edges
N: largest weight magnitude
Table of Algorithms
| Name | Year | Time | Space | Approximation Factor | Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
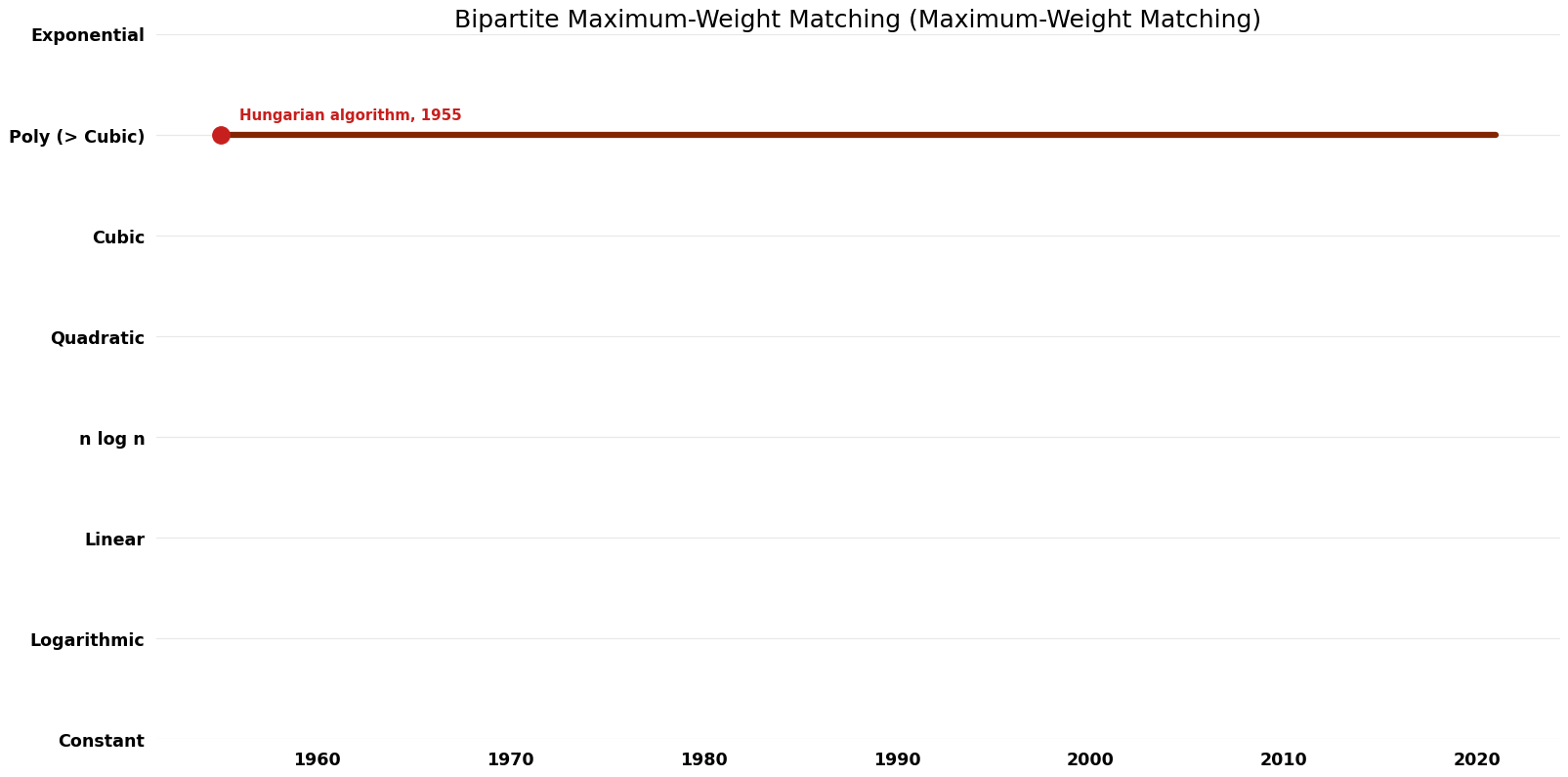
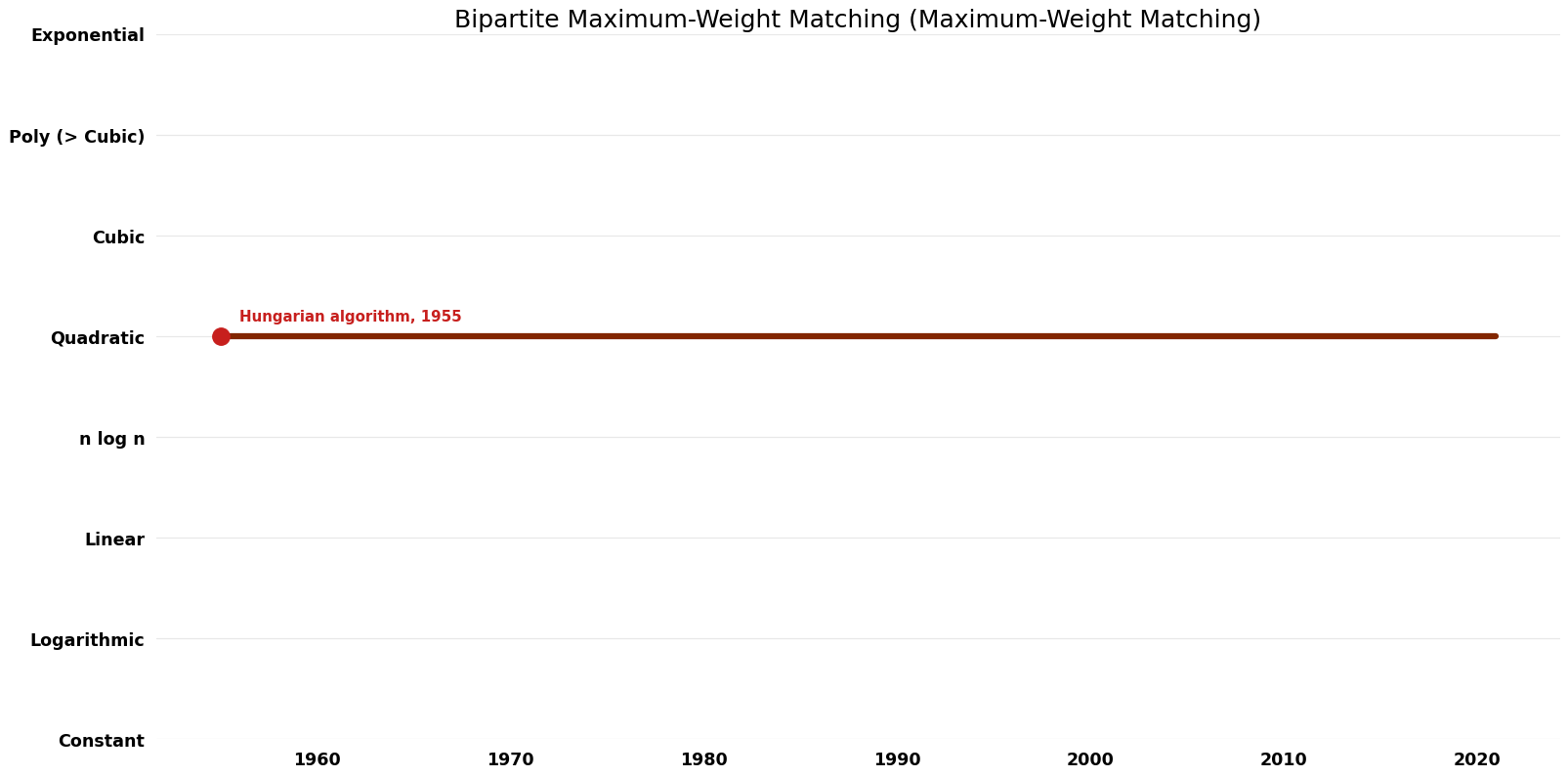
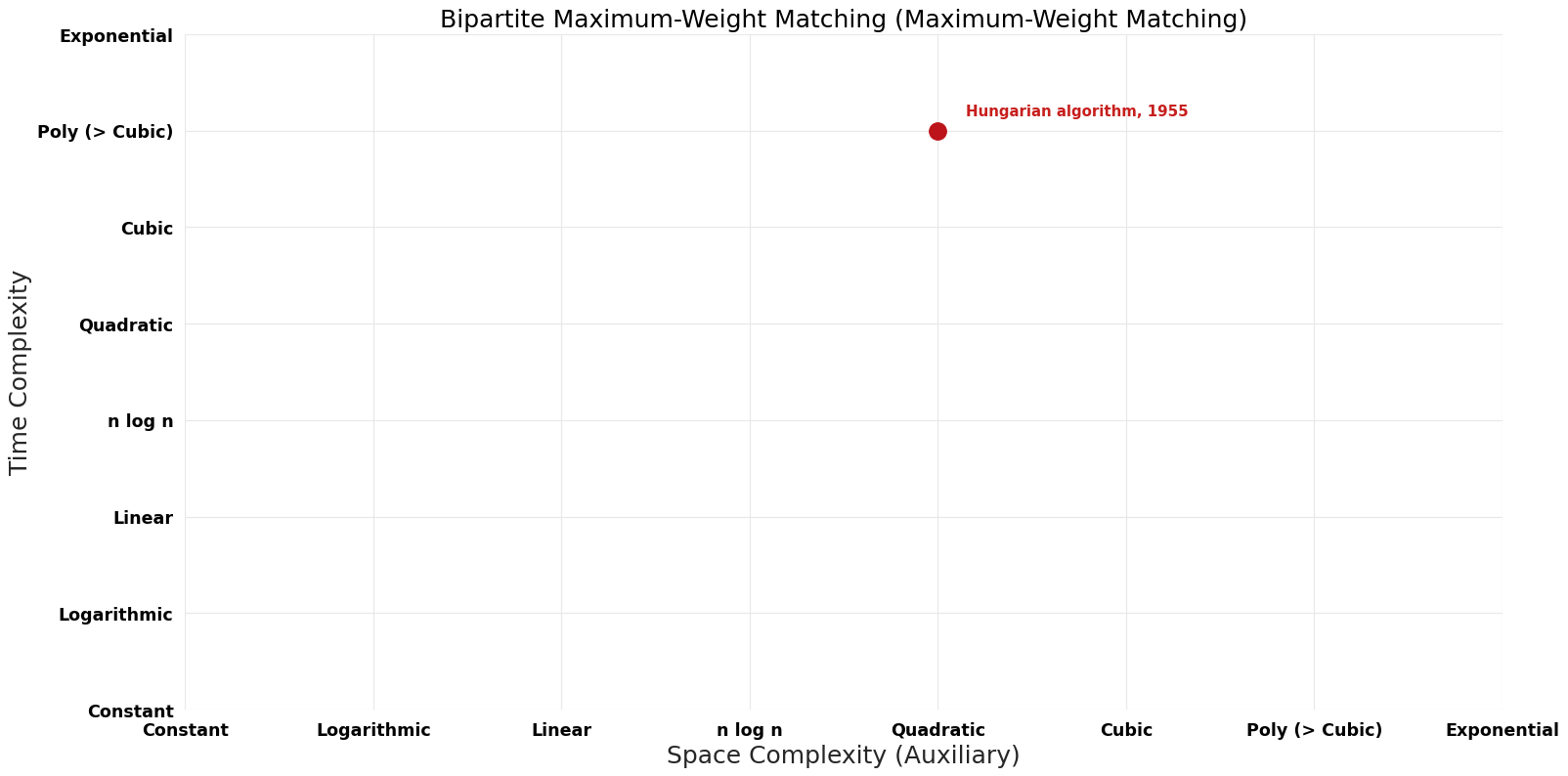
| Hungarian algorithm | 1955 | $O(n^{4})$ | $O(n^{2})$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Micali; Vazirani | 1980 | $O(n^{3} logn)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time | |
| Mucha and Sankowski | 2004 | $O(n^{3})$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |