Lossy Compression: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "{{DISPLAYTITLE:Lossy Compression (Data Compression)}} == Description == The reduction or ideally elimination of redundancies in the original data to result in smaller required storage space is the goal of every compression scheme. There are two categories of data compression: lossy and lossless. Lossy compression is achieved by only discarding the redundancies and out of human perception information and getting rid of those extra bits. == Related Problems == Relat...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
|} | |} | ||
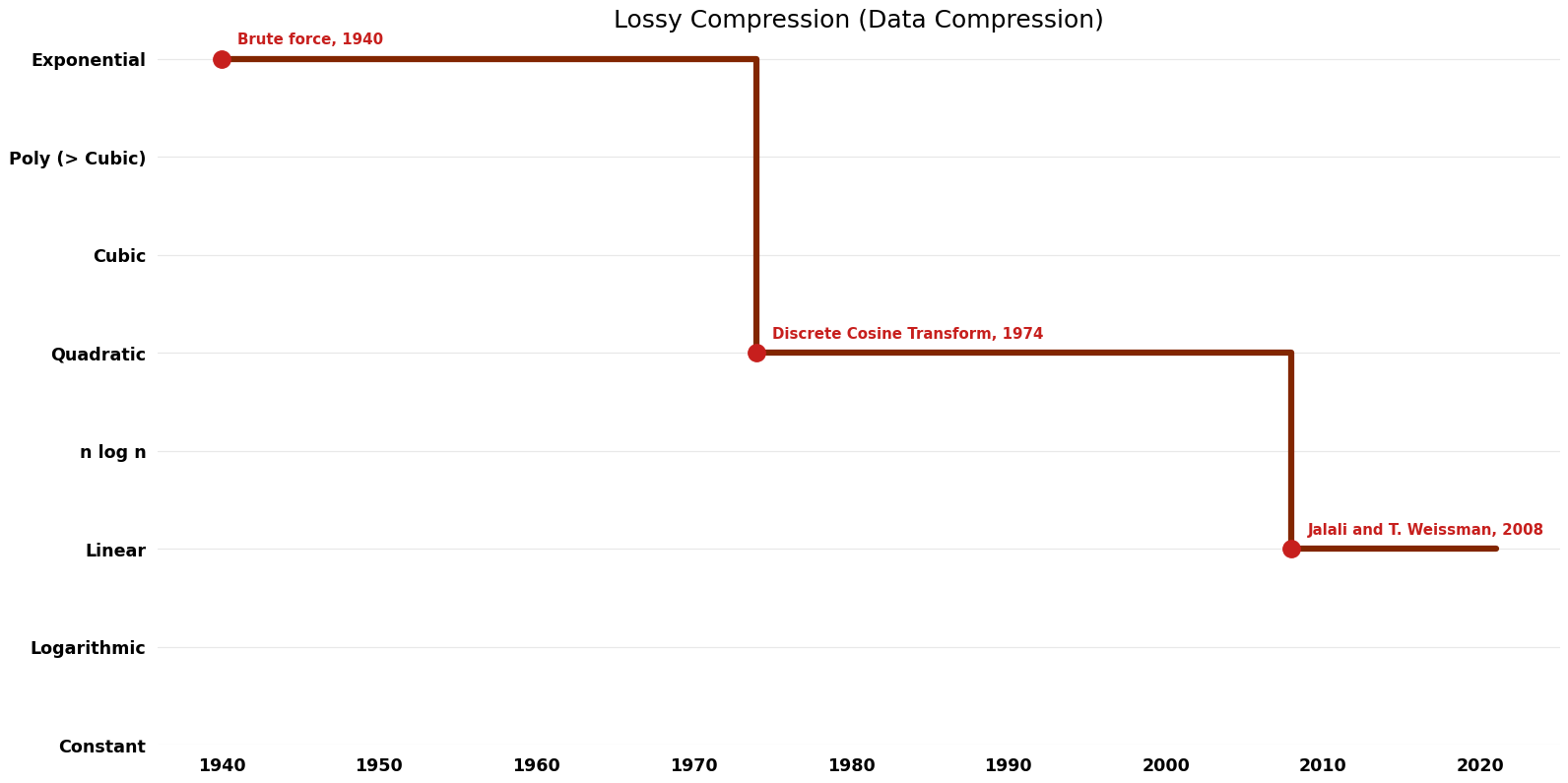
== Time Complexity | == Time Complexity Graph == | ||
[[File:Data Compression - Lossy Compression - Time.png|1000px]] | [[File:Data Compression - Lossy Compression - Time.png|1000px]] | ||
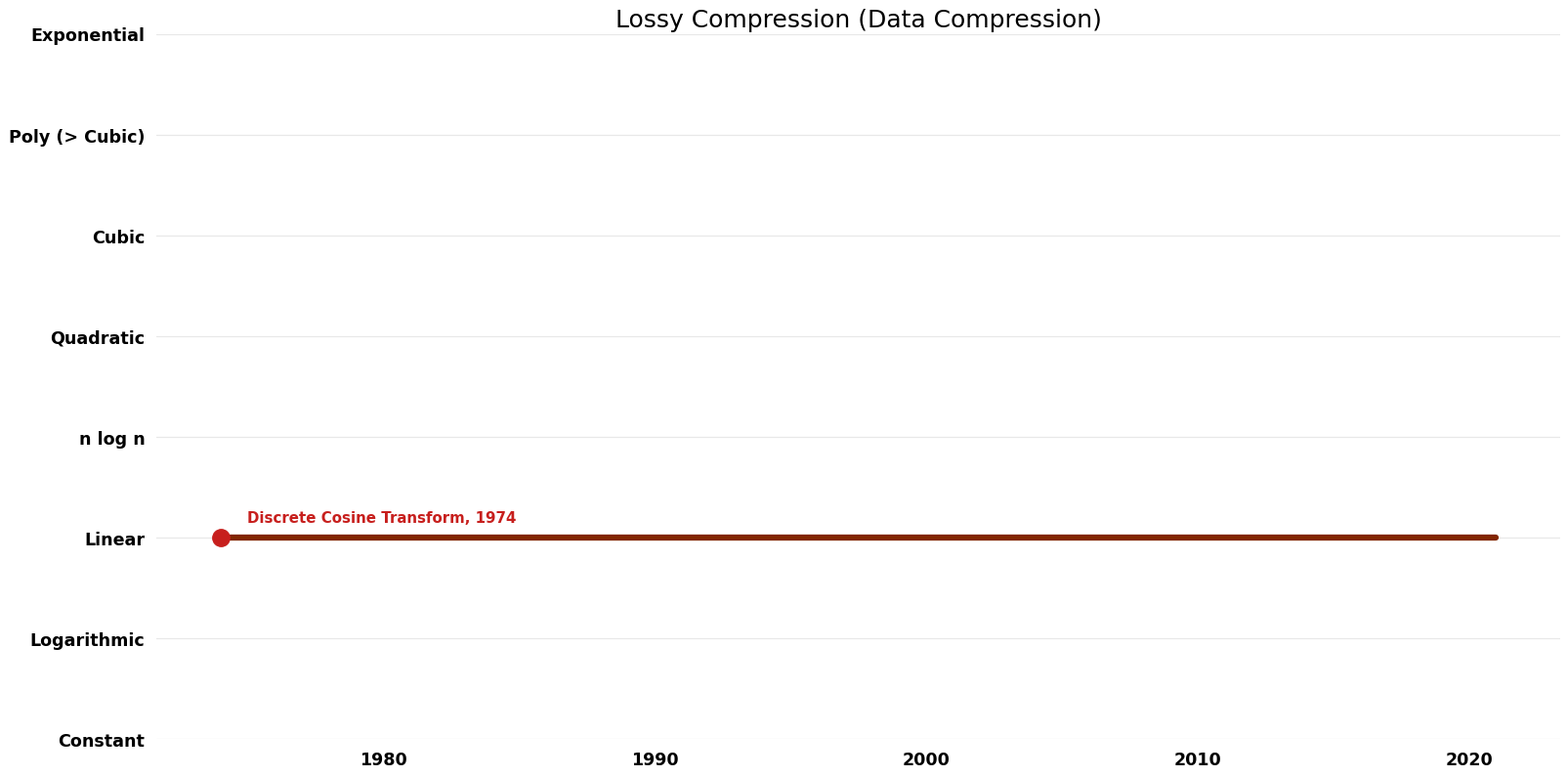
== Space Complexity | == Space Complexity Graph == | ||
[[File:Data Compression - Lossy Compression - Space.png|1000px]] | [[File:Data Compression - Lossy Compression - Space.png|1000px]] | ||
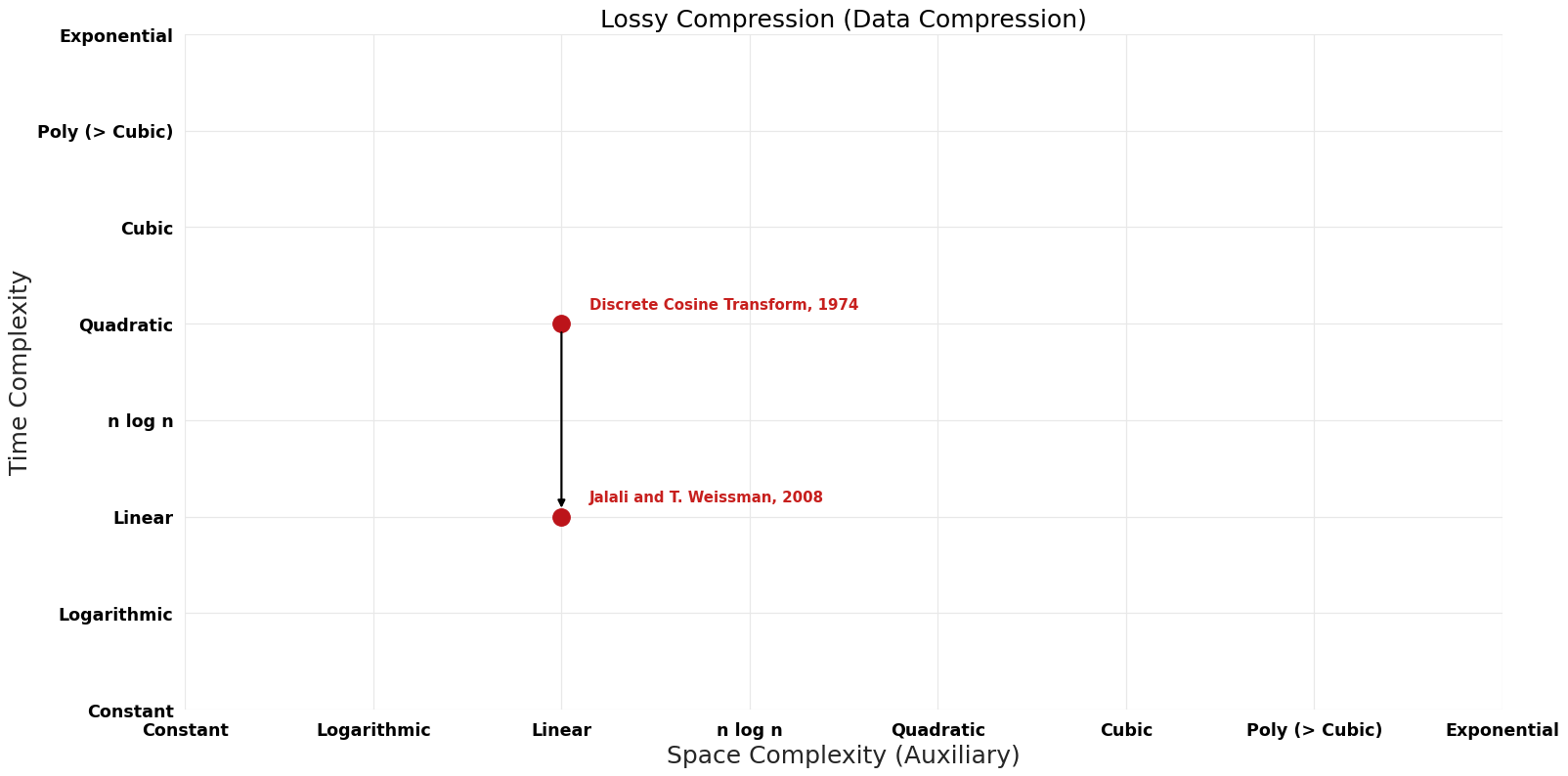
== Pareto | == Pareto Frontier Improvements Graph == | ||
[[File:Data Compression - Lossy Compression - Pareto Frontier.png|1000px]] | [[File:Data Compression - Lossy Compression - Pareto Frontier.png|1000px]] | ||
Revision as of 14:04, 15 February 2023
Description
The reduction or ideally elimination of redundancies in the original data to result in smaller required storage space is the goal of every compression scheme. There are two categories of data compression: lossy and lossless.
Lossy compression is achieved by only discarding the redundancies and out of human perception information and getting rid of those extra bits.
Related Problems
Related: Lossless Compression
Parameters
No parameters found.
Table of Algorithms
| Name | Year | Time | Space | Approximation Factor | Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gupta; Verdu | 2009 | $O(n^{2} log^{3} n)$ | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Discrete Cosine Transform | 1974 | $O(n^{2})$ | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Maneva and M. J. Wainwright | 2005 | $O(n^{2})$ | $O(n^{2})$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Ciliberti; Mézard | 2005 | $O(n^{2})$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time | |
| Brute force | 1940 | $O(n*{2}^n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | ||
| Matsunaga; Yamamoto | 2003 | $O(n*{2}^n)$ | exp(n) | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
| Sun; M. Shao; J. Chen; K. Wong; and X. Wu | 2010 | $O(n*{2}^n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time | |
| Miyake | 2006 | $O(n*{2}^n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time | |
| Martinian and M. J. Wainwright | 2006 | $O(n*{2}^n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time | |
| Jalali and T. Weissman | 2008 | $O(n)$ | $O(n)$? | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Jalali; A. Montanari; and T. Weissman | 2010 | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time | |
| Korada and R. Urbanke; | 2010 | $O(n*{2}^n)$ | $O(N)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |