Entity Resolution: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
$n$: number of records | |||
$k$: number of features | |||
== Table of Algorithms == | == Table of Algorithms == | ||
| Line 16: | Line 18: | ||
|- | |- | ||
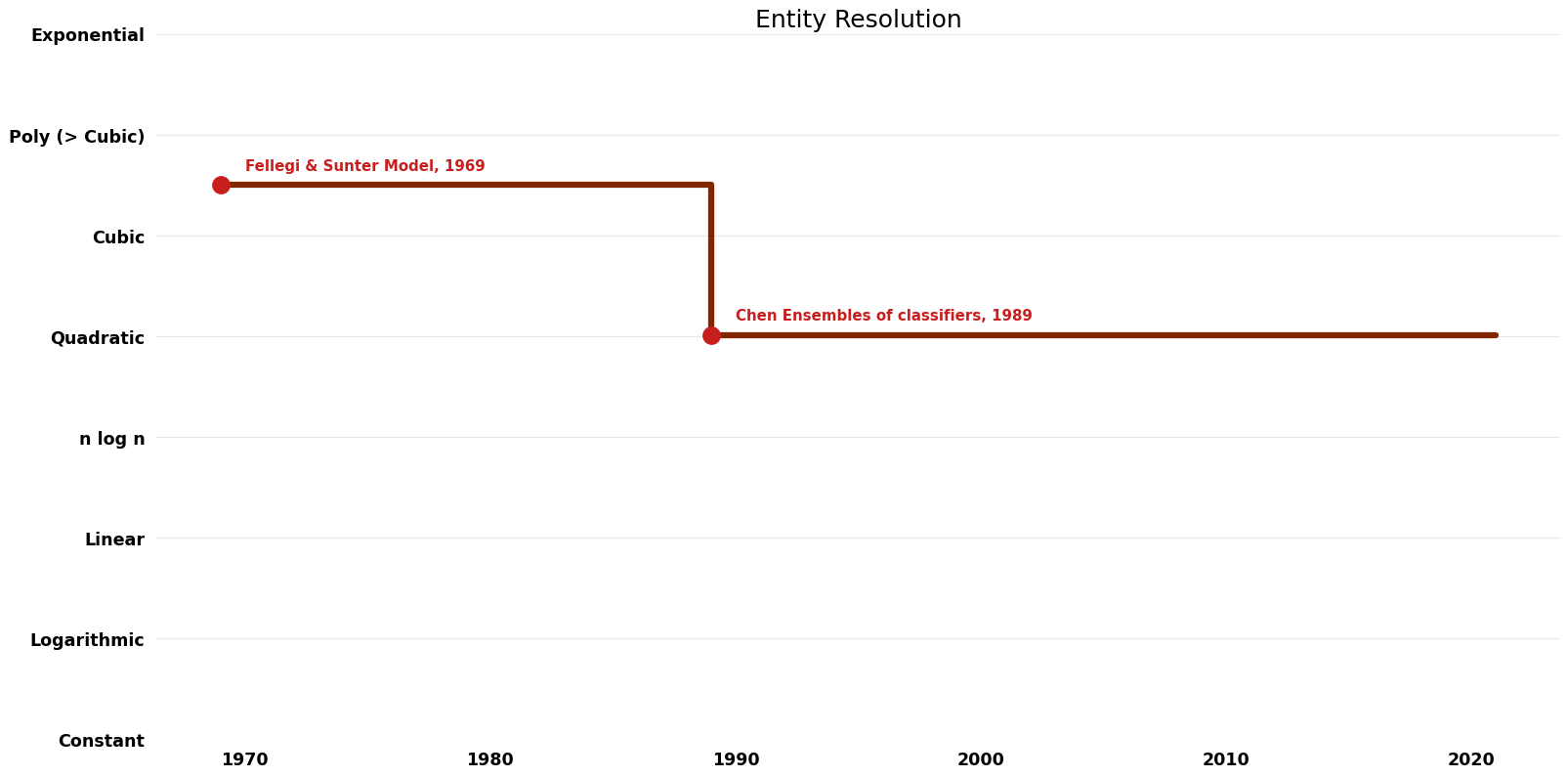
| [[Fellegi & Sunter Model (Entity Resolution Entity Resolution)|Fellegi & Sunter Model]] || 1969 || $O(n^{3}k)$ || | | [[Fellegi & Sunter Model (Entity Resolution Entity Resolution)|Fellegi & Sunter Model]] || 1969 || $O(n^{3}k)$ || $O(k)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/cse590q/04au/papers/Felligi69.pdf Time] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Gupta & Sarawagi CRF (Entity Resolution Entity Resolution)|Gupta & Sarawagi CRF]] || 2009 || $O(n^{3}k)$ || | | [[Gupta & Sarawagi CRF (Entity Resolution Entity Resolution)|Gupta & Sarawagi CRF]] || 2009 || $O(n^{3}k)$ || $O(nk)$? || Exact || Deterministic || [https://doi.org/10.14778/1687627.1687661 Time] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Chen Ensembles of classifiers (Entity Resolution Entity Resolution)|Chen Ensembles of classifiers]] || 1989 || $O(n^{2} | | [[Chen Ensembles of classifiers (Entity Resolution Entity Resolution)|Chen Ensembles of classifiers]] || 1989 || $O(n^{2} \log n)$ || || Exact || Deterministic || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[EM Based Winkler (Entity Resolution Entity Resolution)|EM Based Winkler]] || 2000 || $O(n^{3}k)$ || $O(k)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/cse590q/04au/papers/WinklerEM.pdf Time] | | [[EM Based Winkler (Entity Resolution Entity Resolution)|EM Based Winkler]] || 2000 || $O(n^{3}k)$ || $O(k)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/cse590q/04au/papers/WinklerEM.pdf Time] | ||
| Line 26: | Line 28: | ||
| [[Ravikumar & Cohen Generative Models (Entity Resolution Entity Resolution)|Ravikumar & Cohen Generative Models]] || 2004 || $O(n^{2} k)$ || $O(k)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://arxiv.org/abs/1207.4180 Time] | | [[Ravikumar & Cohen Generative Models (Entity Resolution Entity Resolution)|Ravikumar & Cohen Generative Models]] || 2004 || $O(n^{2} k)$ || $O(k)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://arxiv.org/abs/1207.4180 Time] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Bellare Active Learning (Entity Resolution Entity Resolution)|Bellare Active Learning]] || 2012 || $O(n^{2} | | [[Bellare Active Learning (Entity Resolution Entity Resolution)|Bellare Active Learning]] || 2012 || $O(n^{2} \log n c \log c)$ || || Exact || Deterministic || [https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/2339530.2339707 Time] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Ananthakrishna (Entity Resolution Entity Resolution)|Ananthakrishna]] || 2002 || $O(n^{2} k)$ || $O(n)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-155860869-6/50058-5 Time] | | [[Ananthakrishna (Entity Resolution Entity Resolution)|Ananthakrishna]] || 2002 || $O(n^{2} k)$ || $O(n)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-155860869-6/50058-5 Time] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[ | | [[BOYS algorithm (Entity Resolution Entity Resolution)|BOYS algorithm]] || 1993 || $O(n^{2} k)$ || $O(n^{2})$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/016794739390116B Time] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 37: | Line 39: | ||
[[File:Entity Resolution - Time.png|1000px]] | [[File:Entity Resolution - Time.png|1000px]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:10, 28 April 2023
Description
Entity resolution (ER) is the problem of matching records that represent the same real-world entity and then merging the matching records. ER is a well known problem that arises in many applications. An exhaustive ER process involves comparing all the pairs of records, which can be very expensive for large datasets.
Parameters
$n$: number of records
$k$: number of features
Table of Algorithms
| Name | Year | Time | Space | Approximation Factor | Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fellegi & Sunter Model | 1969 | $O(n^{3}k)$ | $O(k)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Gupta & Sarawagi CRF | 2009 | $O(n^{3}k)$ | $O(nk)$? | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Chen Ensembles of classifiers | 1989 | $O(n^{2} \log n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | ||
| EM Based Winkler | 2000 | $O(n^{3}k)$ | $O(k)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Ravikumar & Cohen Generative Models | 2004 | $O(n^{2} k)$ | $O(k)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Bellare Active Learning | 2012 | $O(n^{2} \log n c \log c)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time | |
| Ananthakrishna | 2002 | $O(n^{2} k)$ | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| BOYS algorithm | 1993 | $O(n^{2} k)$ | $O(n^{2})$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |