Greatest Common Divisor: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
Let $a_1, \ldots, | Let $a_1, \ldots, a_m$ be given nonzero integers. Then $g$ is called the greatest common divisor (GCD) of $a_1, \ldots, a_m$ if and only if it is the largest integer that divides all $a_1, \ldots, a_m$. | ||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
n: number of integers | $n$: sum of number of bits among the integers | ||
== Table of Algorithms == | == Table of Algorithms == | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
| [[Binary GCD algorithm (Greatest Common Divisor Greatest Common Divisor)|Binary GCD algorithm]] || 1967 || $O(n^{2})$ || $O(n)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://arxiv.org/abs/0910.0095 Time] | | [[Binary GCD algorithm (Greatest Common Divisor Greatest Common Divisor)|Binary GCD algorithm]] || 1967 || $O(n^{2})$ || $O(n)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://arxiv.org/abs/0910.0095 Time] | ||
|- | |- | ||
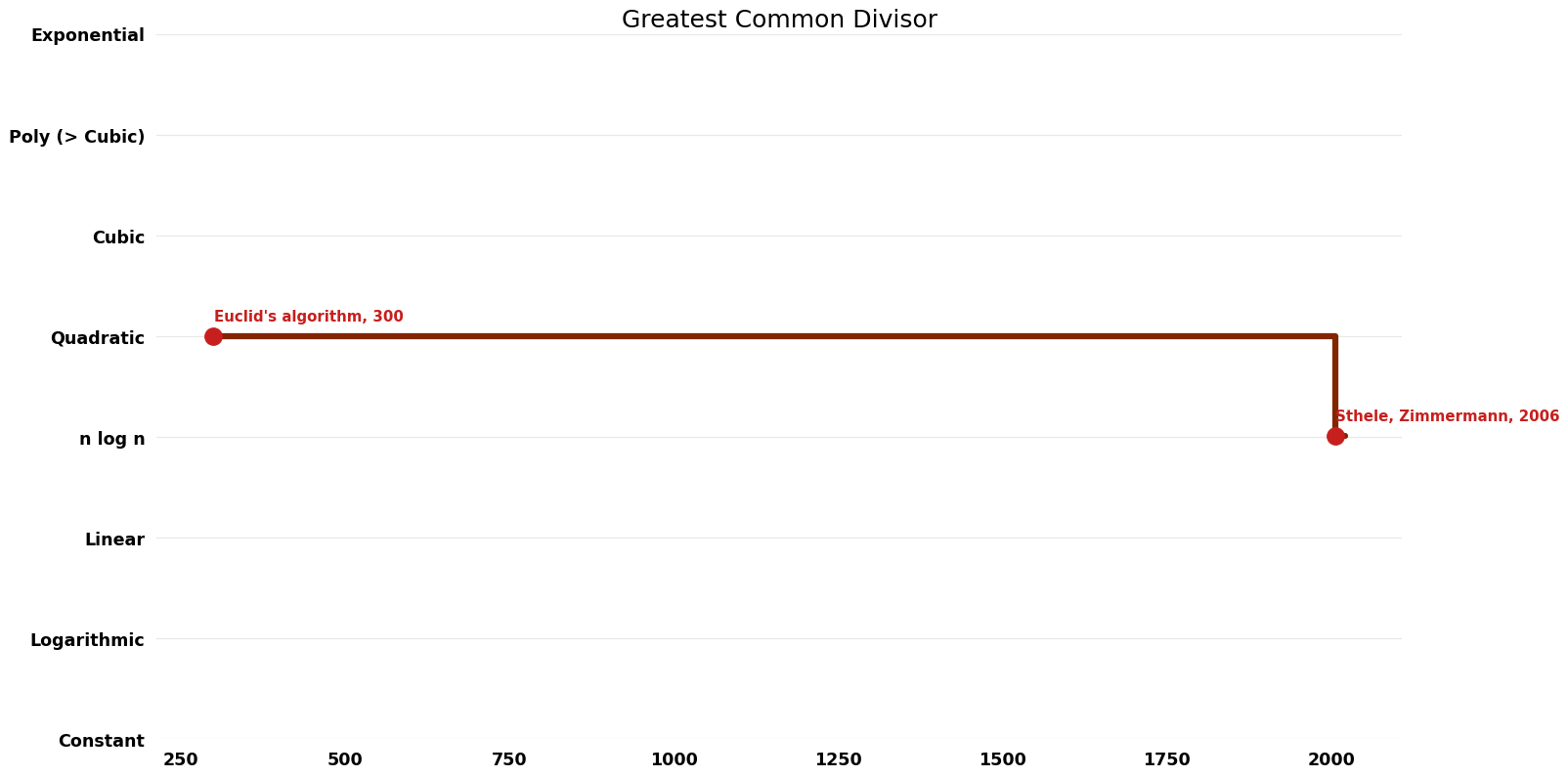
| [[Sthele, Zimmermann (Greatest Common Divisor Greatest Common Divisor)|Sthele, Zimmermann]] || 2006 || $O(n log^{2} n log log n)$ || $O(n)$?? || Exact || Deterministic || [https://hal.inria.fr/file/index/docid/71533/filename/RR-5050.pdf Time] | | [[Sthele, Zimmermann (Greatest Common Divisor Greatest Common Divisor)|Sthele, Zimmermann]] || 2006 || $O(n \log^{2} n \log \log n)$ || $O(n)$?? || Exact || Deterministic || [https://hal.inria.fr/file/index/docid/71533/filename/RR-5050.pdf Time] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
[[File:Greatest Common Divisor - Time.png|1000px]] | [[File:Greatest Common Divisor - Time.png|1000px]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:12, 28 April 2023
Description
Let $a_1, \ldots, a_m$ be given nonzero integers. Then $g$ is called the greatest common divisor (GCD) of $a_1, \ldots, a_m$ if and only if it is the largest integer that divides all $a_1, \ldots, a_m$.
Parameters
$n$: sum of number of bits among the integers
Table of Algorithms
| Name | Year | Time | Space | Approximation Factor | Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Euclid's algorithm | -300 | $O(n^{2})$ | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | |
| Lehmer's GCD algorithm | 1940 | $O(n^{2})$ | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | |
| Binary GCD algorithm | 1967 | $O(n^{2})$ | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Sthele, Zimmermann | 2006 | $O(n \log^{2} n \log \log n)$ | $O(n)$?? | Exact | Deterministic | Time |