Duplicate Elimination: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "== Problem Description== SQL does not eliminate duplicates implicitly. It allows to enter duplicate values on columns other than candidate key or if did not specified any keys. If the user wants to eliminate duplicate records, he has to use DISTINCT keyword in the query. Databases, therefore, can have duplicate entries. The problem deals with identifying and removing duplicates from a database. == Bounds Chart == 1050px ==...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== | {{DISPLAYTITLE:Duplicate Elimination (Duplicate Elimination)}} | ||
== Description == | |||
SQL does not eliminate duplicates implicitly. It allows to enter duplicate values on columns other than candidate key or if did not specified any keys. If the user wants to eliminate duplicate records, he has to use DISTINCT keyword in the query. | SQL does not eliminate duplicates implicitly. It allows to enter duplicate values on columns other than candidate key or if did not specified any keys. If the user wants to eliminate duplicate records, he has to use DISTINCT keyword in the query. | ||
Databases, therefore, can have duplicate entries. The problem deals with identifying and removing duplicates from a database. | Databases, therefore, can have duplicate entries. The problem deals with identifying and removing duplicates from a database. | ||
== | == Parameters == | ||
$n$: number of records | |||
== Table of Algorithms == | |||
== | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align:center;" width="100%" | ||
! Name !! Year !! Time !! Space !! Approximation Factor !! Model !! Reference | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | |||
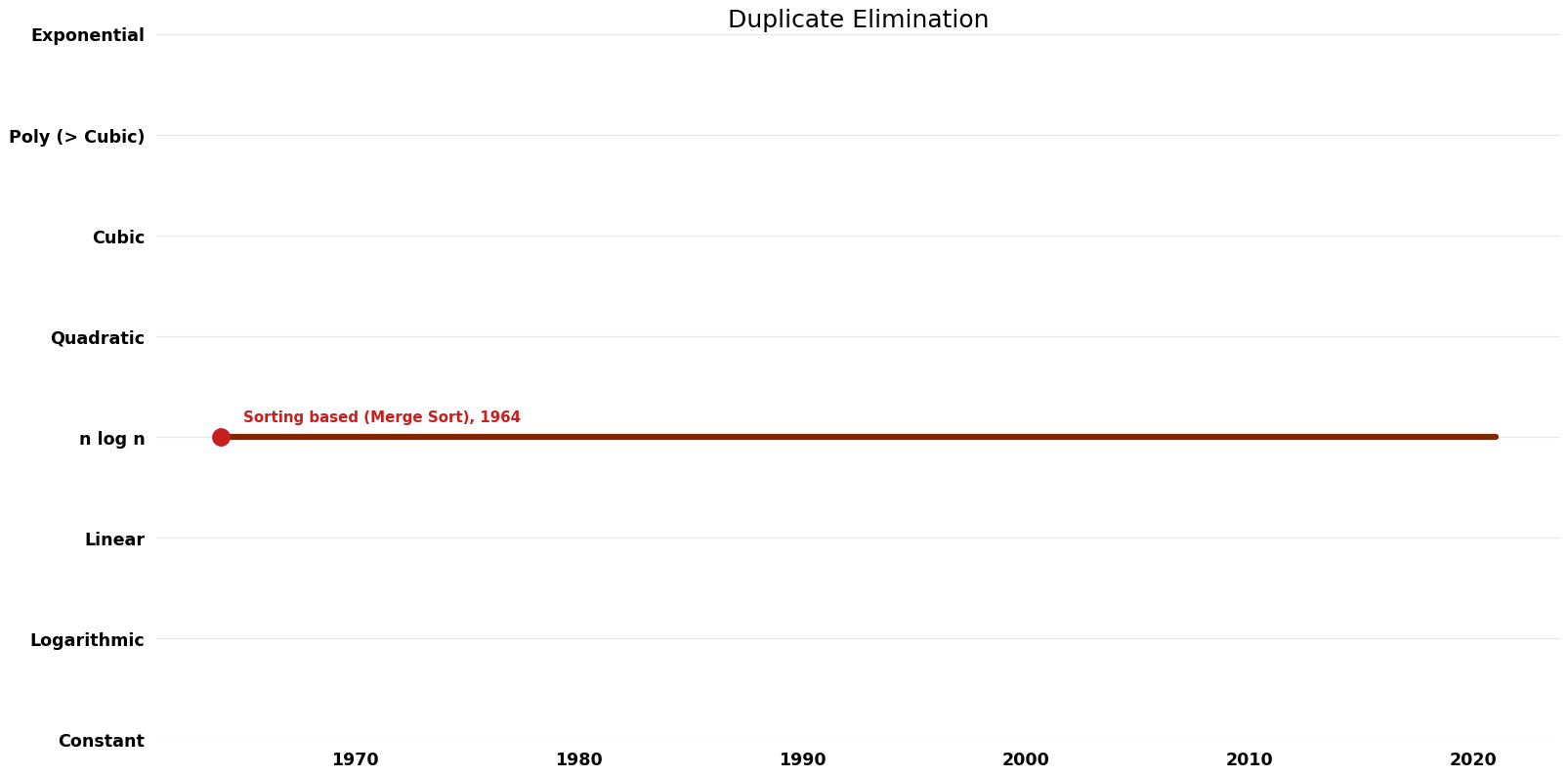
| | | [[Sorting based (Merge Sort) (Duplicate Elimination Duplicate Elimination)|Sorting based (Merge Sort)]] || 1964 || $O(n \log n)$ || $O(n)$ || Exact || Deterministic || | ||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[Sorting based (Merge Sort) + real-time elimination (Duplicate Elimination Duplicate Elimination)|Sorting based (Merge Sort) + real-time elimination]] || 1964 || $O(n \log n)$ || || Exact || Deterministic || | ||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[BST Algorithm (Duplicate Elimination Duplicate Elimination)|BST Algorithm]] || 1999 || $O(n \log n)$ || $O(\log n)$ || Exact || Deterministic || | ||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[Priority Queue Algorithm (Duplicate Elimination Duplicate Elimination)|Priority Queue Algorithm]] || 1976 || $O(n^{2})$ || $O(n)$ || Exact || Deterministic || | ||
| [ | |- | ||
| [[Sorted Neighborhood Algorithm (SNA) (Duplicate Elimination Duplicate Elimination)|Sorted Neighborhood Algorithm (SNA)]] || 1998 || $O(n^{2})$ || $O(n)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1009761603038 Time] | |||
[ | |- | ||
| [[Duplicate Elimination Sorted Neighborhood Algorithm (DE-SNA) (Duplicate Elimination Duplicate Elimination)|Duplicate Elimination Sorted Neighborhood Algorithm (DE-SNA)]] || 2002 || $O(n \log n)$ || || Exact || Deterministic || | |||
[ | |- | ||
| [[Adaptive Duplicate Detection Algorithm (ADD) (Duplicate Elimination Duplicate Elimination)|Adaptive Duplicate Detection Algorithm (ADD)]] || 2003 || $O(n^{3})$ || $O({1})$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/956750.956759 Time] | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
== Time Complexity Graph == | |||
[ | [[File:Duplicate Elimination - Time.png|1000px]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:10, 28 April 2023
Description
SQL does not eliminate duplicates implicitly. It allows to enter duplicate values on columns other than candidate key or if did not specified any keys. If the user wants to eliminate duplicate records, he has to use DISTINCT keyword in the query.
Databases, therefore, can have duplicate entries. The problem deals with identifying and removing duplicates from a database.
Parameters
$n$: number of records
Table of Algorithms
| Name | Year | Time | Space | Approximation Factor | Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sorting based (Merge Sort) | 1964 | $O(n \log n)$ | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | |
| Sorting based (Merge Sort) + real-time elimination | 1964 | $O(n \log n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | ||
| BST Algorithm | 1999 | $O(n \log n)$ | $O(\log n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | |
| Priority Queue Algorithm | 1976 | $O(n^{2})$ | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | |
| Sorted Neighborhood Algorithm (SNA) | 1998 | $O(n^{2})$ | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Duplicate Elimination Sorted Neighborhood Algorithm (DE-SNA) | 2002 | $O(n \log n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | ||
| Adaptive Duplicate Detection Algorithm (ADD) | 2003 | $O(n^{3})$ | $O({1})$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |