Key Exchange: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
n: maximum size of numbers (prime, parameters, keys), in bits | $n$: maximum size of numbers (prime, parameters, keys), in bits | ||
== Table of Algorithms == | == Table of Algorithms == | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
[[File:Key Exchange - Time.png|1000px]] | [[File:Key Exchange - Time.png|1000px]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:07, 28 April 2023
Description
Key exchange (also key establishment) is a method in cryptography by which cryptographic keys are exchanged between two parties, allowing use of a cryptographic algorithm.
Parameters
$n$: maximum size of numbers (prime, parameters, keys), in bits
Table of Algorithms
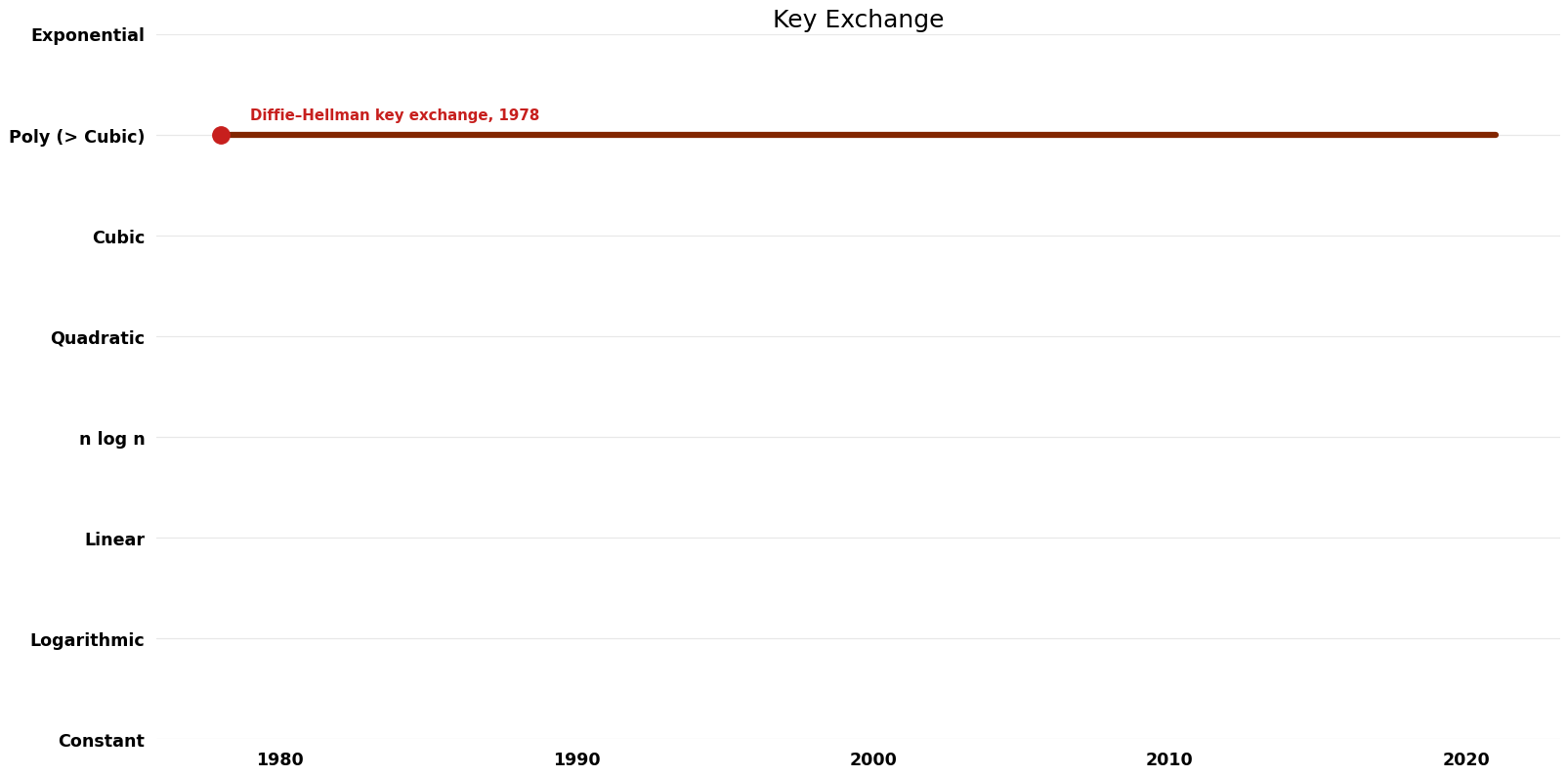
| Name | Year | Time | Space | Approximation Factor | Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffie–Hellman key exchange | 1978 | $O(mult(n)$*n) where mult(n) is running time on n-bit multiplication | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Elliptic-curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH) | 2006 | $O(mult(n)$*n^{2})? where mult(n) is running time on n-bit multiplication | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |