Subset Sum: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
S: the set of integers | $S$: the set of integers | ||
n: the number of integers in the set | $n$: the number of integers in the set | ||
n': the number of distinct elements in the set | $n'$: the number of distinct elements in the set | ||
t: the target sum | $t$: the target sum | ||
$\sigma$: sum of elements in the set | |||
== Table of Algorithms == | == Table of Algorithms == | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
| [[Klinz (Subset Sum The Subset-Sum Problem)|Klinz]] || 1999 || $O(σ^{({3}/{2})})$ || $O(t)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0037(199905)33:3%3C189::AID-NET5%3E3.0.CO;2-2 Time] & [https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3329863, Space] | | [[Klinz (Subset Sum The Subset-Sum Problem)|Klinz]] || 1999 || $O(σ^{({3}/{2})})$ || $O(t)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0037(199905)33:3%3C189::AID-NET5%3E3.0.CO;2-2 Time] & [https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3329863, Space] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[ | | [[Eppstein (Subset Sum The Subset-Sum Problem)|Eppstein]] || 1997 || $\tilde{O}(n max(S))$ || $O(t logt)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S019667749690841X?via%3Dihub Time] & [https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3329863, Space] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Serang (Subset Sum The Subset-Sum Problem)|Serang]] || 2014 || $\tilde{O}(n max(S))$ || $O(t logt)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0091507 Time] & [https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3329863, Space] | | [[Serang (Subset Sum The Subset-Sum Problem)|Serang]] || 2014 || $\tilde{O}(n max(S))$ || $O(t logt)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0091507 Time] & [https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3329863, Space] | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
| [[Bringman (Subset Sum The Subset-Sum Problem)|Bringman]] || 2017 || $\tilde{O}(nt^{1+\epsilon})$ || \tilde{O}(nt^\epsilon) || (n+t)^{-\Omega(1)} error || Randomized || [https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.04712 Time & Space] | | [[Bringman (Subset Sum The Subset-Sum Problem)|Bringman]] || 2017 || $\tilde{O}(nt^{1+\epsilon})$ || \tilde{O}(nt^\epsilon) || (n+t)^{-\Omega(1)} error || Randomized || [https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.04712 Time & Space] | ||
|- | |- | ||
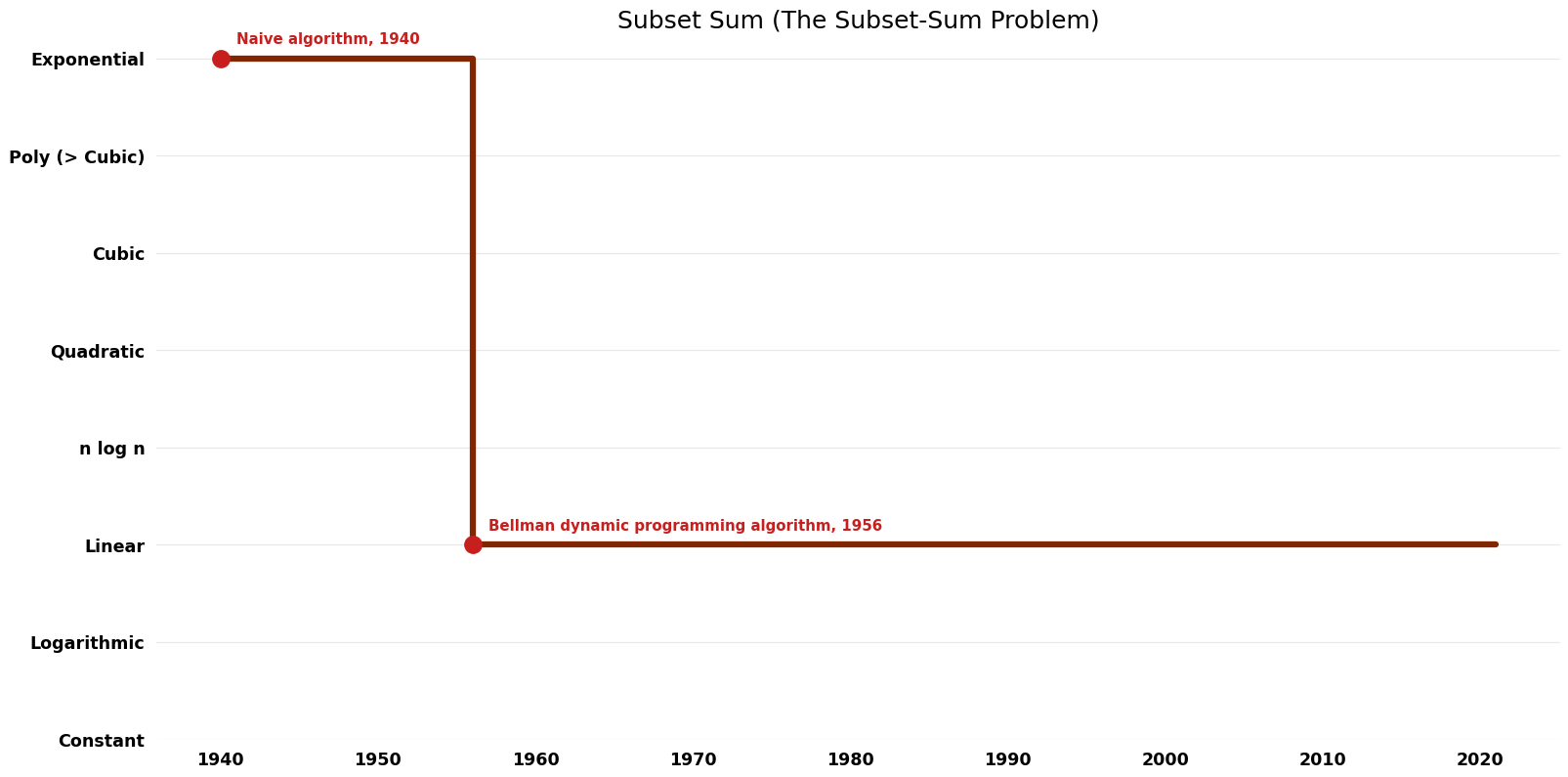
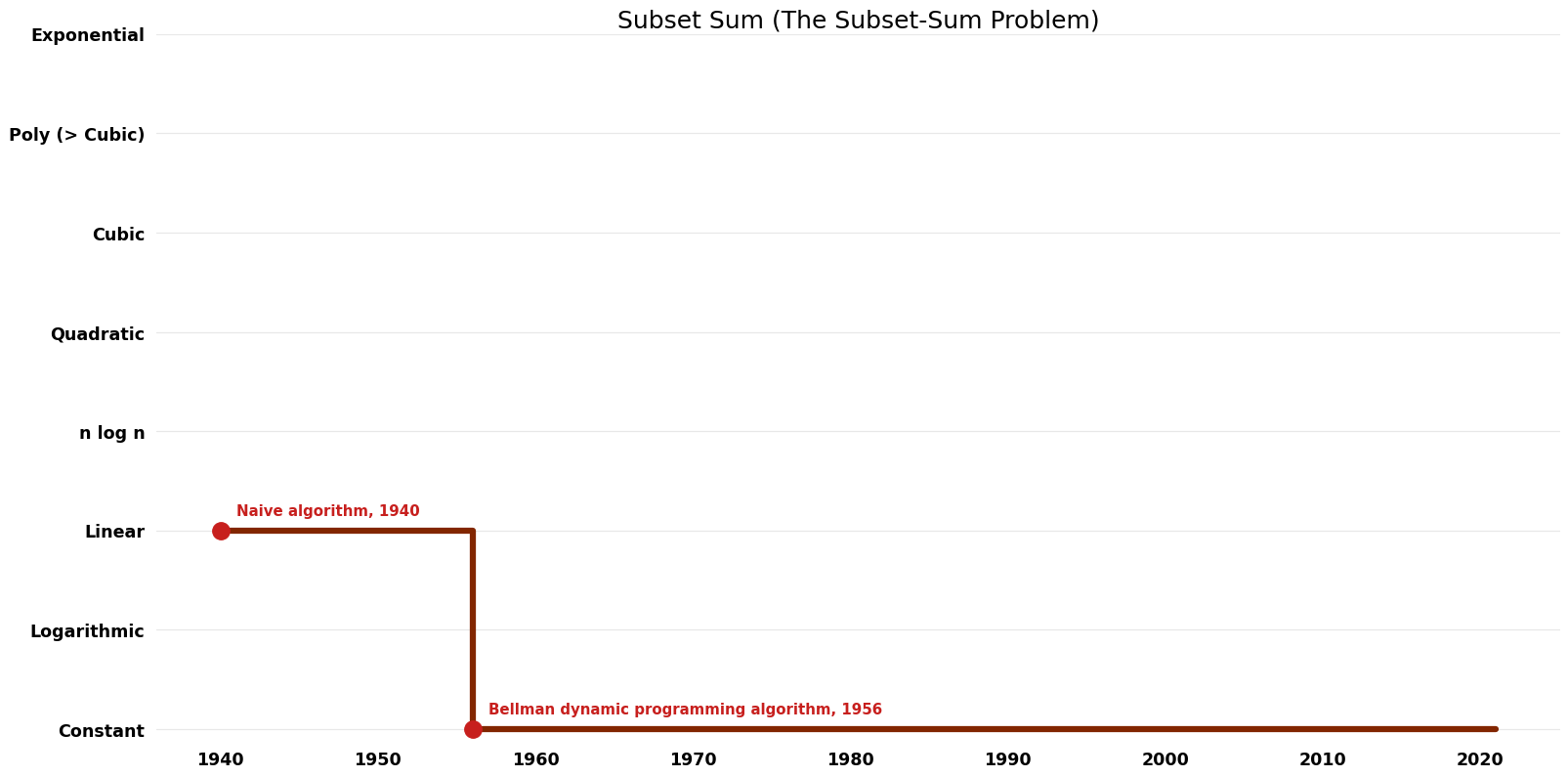
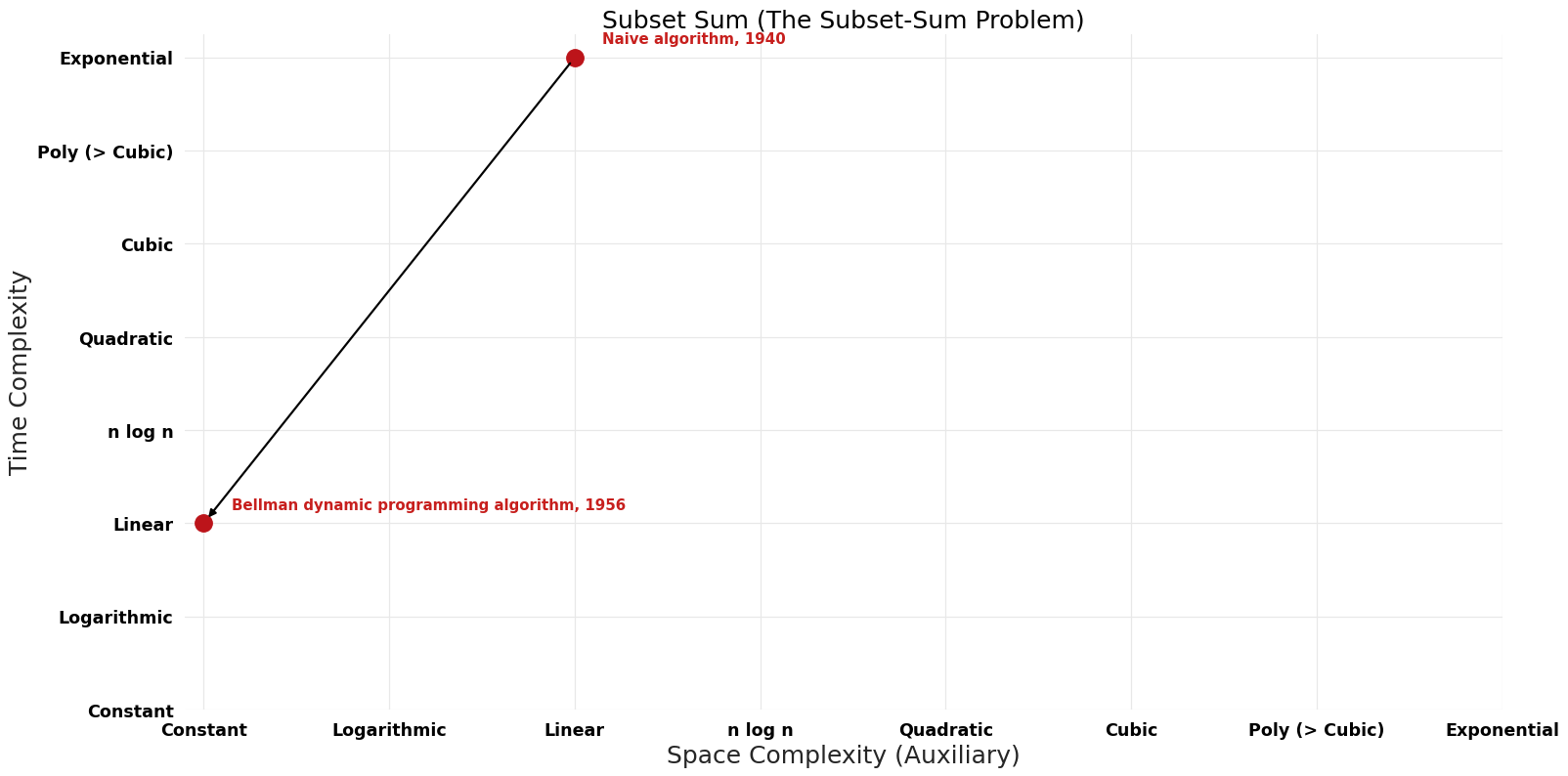
| [[Naive algorithm (Subset Sum The Subset-Sum Problem)|Naive algorithm]] || 1940 || $O({2}^n * n)$ || $O(n)$ | | [[Naive algorithm (Subset Sum The Subset-Sum Problem)|Naive algorithm]] || 1940 || $O({2}^n * n)$ || $O(n)$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/321812.321823 Space] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Random Split Exponential algorithm (Subset Sum The Subset-Sum Problem)|Random Split Exponential algorithm]] || 1940 || $O({2}^{(n/{2})} * n)$ || $O({2}^{(n/{2})})$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/321812.321823 Space] | | [[Random Split Exponential algorithm (Subset Sum The Subset-Sum Problem)|Random Split Exponential algorithm]] || 1940 || $O({2}^{(n/{2})} * n)$ || $O({2}^{(n/{2})})$ || Exact || Deterministic || [https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/321812.321823 Space] | ||
Revision as of 09:22, 10 April 2023
Description
Given a set $S$ of integers and a target sum $t$, determine whether there is a subset of $S$ that sum to $t$.
Parameters
$S$: the set of integers
$n$: the number of integers in the set
$n'$: the number of distinct elements in the set
$t$: the target sum
$\sigma$: sum of elements in the set
Table of Algorithms
| Name | Year | Time | Space | Approximation Factor | Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pisinger | 2003 | $O(nt/logt)$ | $O(t/logt)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
| Faaland | 1973 | $O(n' t)$ | $O(t)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
| Pferschy | 1999 | $O(n' t)$ | $O(t)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
| Klinz | 1999 | $O(σ^{({3}/{2})})$ | $O(t)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
| Eppstein | 1997 | $\tilde{O}(n max(S))$ | $O(t logt)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
| Serang | 2014 | $\tilde{O}(n max(S))$ | $O(t logt)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
| Serang | 2015 | $\tilde{O}(n max(S))$ | $O(t logt)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
| Lokshtanov | 2010 | $\tilde{O}(n^{3} t)$ | $O(n^{2})$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
| Horowitz and Sahni | 1974 | $O({2}^{(n/{2})})$ | $O({2}^{(n/{2})$}) | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
| Bellman dynamic programming algorithm | 1956 | $O(n t)$ | $O(t)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
| Psinger | 1999 | $O(n max(S))$ | $O(t)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
| Koiliaris and Xu | 2019 | $\tilde{O}(min{\sqrt{n'}t, t^{5/4}, σ})$ | $O(t)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
| Bringman | 2017 | $\tilde{O}(nt^{1+\epsilon})$ | \tilde{O}(nt^\epsilon) | (n+t)^{-\Omega(1)} error | Randomized | Time & Space |
| Naive algorithm | 1940 | $O({2}^n * n)$ | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Space |
| Random Split Exponential algorithm | 1940 | $O({2}^{(n/{2})} * n)$ | $O({2}^{(n/{2})})$ | Exact | Deterministic | Space |
Time Complexity Graph
Space Complexity Graph
Time-Space Tradeoff
Reductions FROM Problem
| Problem | Implication | Year | Citation | Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k-SAT | assume: SETH then: for any $\epsilon > {0}$ there exists a $\delta > {0}$ such that Subset Sum is not in time $O(T^{1-\epsilon}{2}^{\delta n})$, and $k$-Sum is not in time $O(T^{1-\epsilon}n^{\delta k})$ |
2022 | https://dl.acm.org/doi/full/10.1145/3450524 | link |