Cycle Detection: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
[[File:Cycle Detection - Space.png|1000px]] | [[File:Cycle Detection - Space.png|1000px]] | ||
== | == Space-Time Tradeoff Improvements == | ||
[[File:Cycle Detection - Pareto Frontier.png|1000px]] | [[File:Cycle Detection - Pareto Frontier.png|1000px]] | ||
Revision as of 15:36, 15 February 2023
Description
Cycle detection or cycle finding is the algorithmic problem of finding a cycle in a sequence of iterated function values.
Parameters
t_f: time to perform one evaluation of f
\mu: the starting index of the cycle
\lambda: the period of the cycle
M: number of values stored
Table of Algorithms
| Name | Year | Time | Space | Approximation Factor | Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sedgewick; Szymanski; and Yao | 1982 | $(\mu + \lambda)({1}+\Theta({1}/sqrt(M)))$ | M | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
| Nivasch | 2004 | $O(\mu + \lambda)$ | $O(logn)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
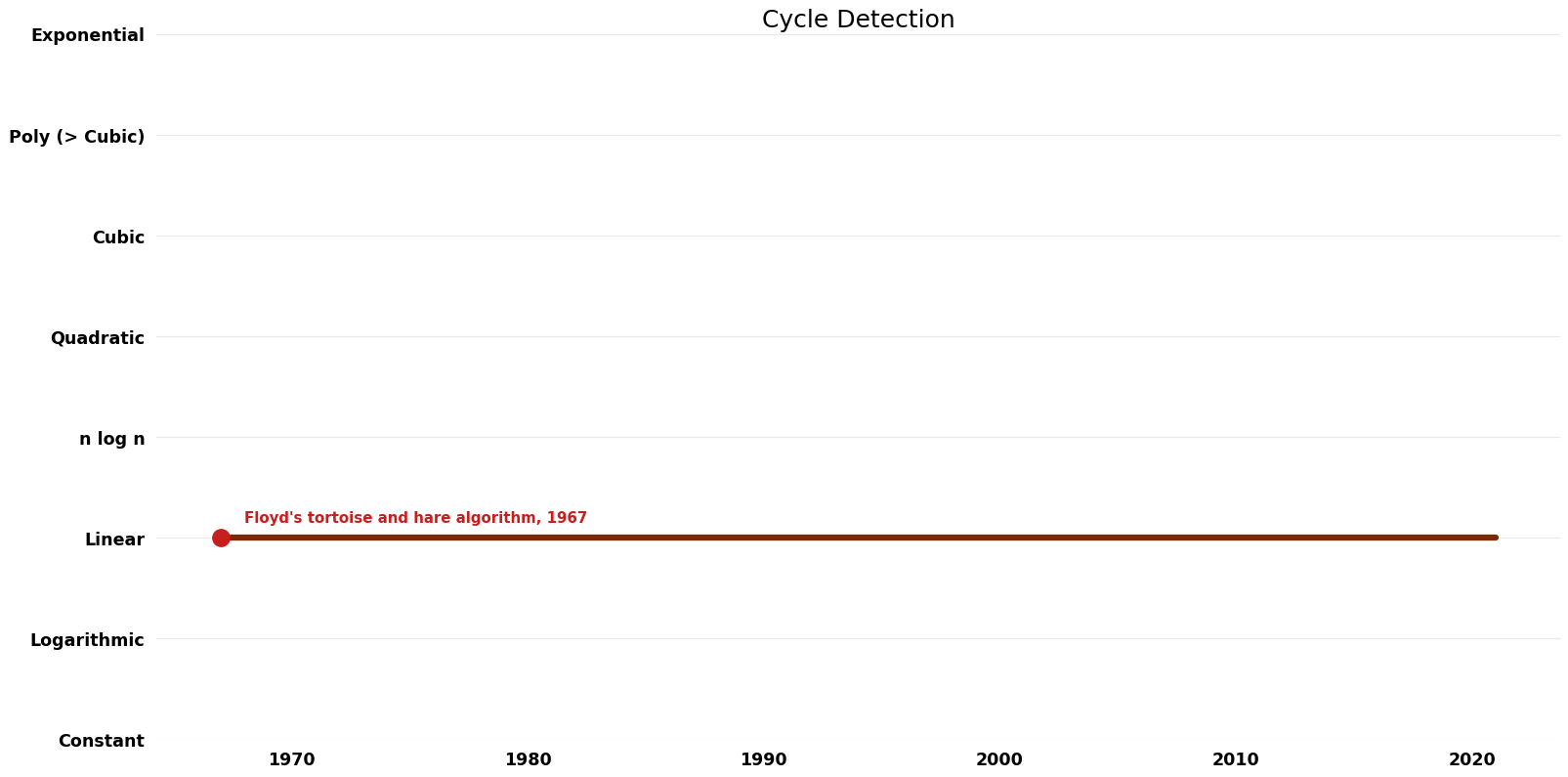
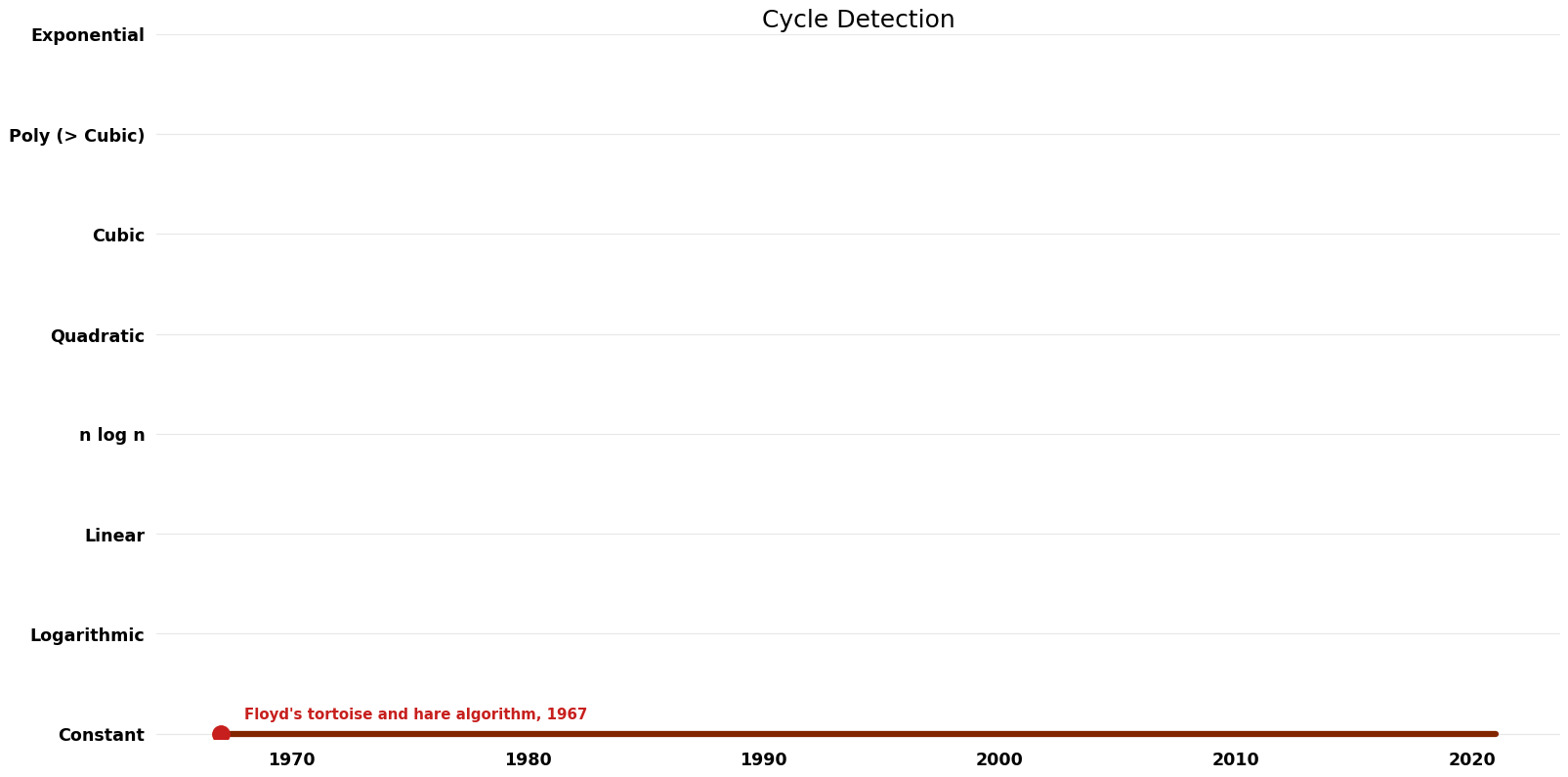
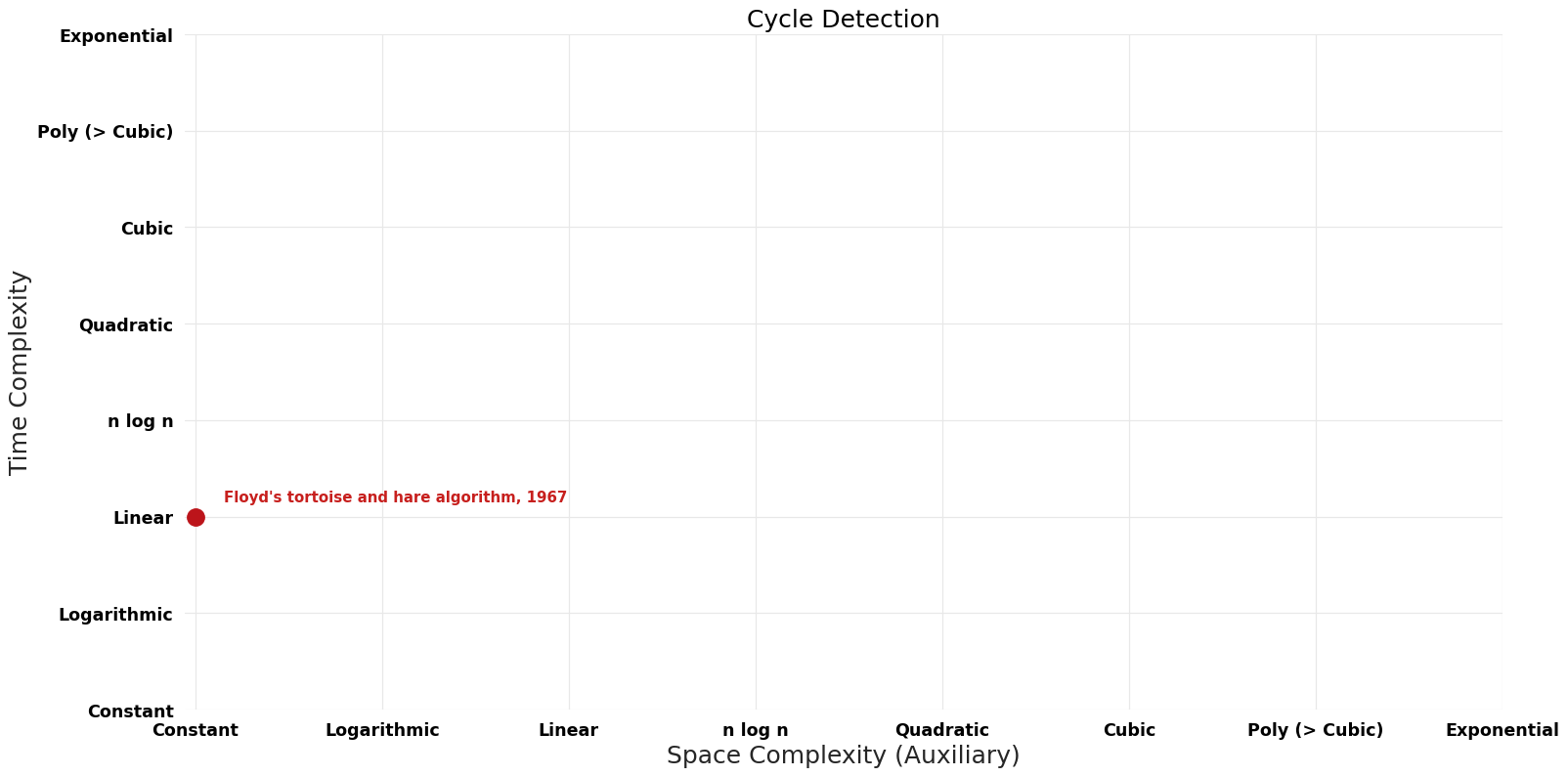
| Floyd's tortoise and hare algorithm | 1967 | $O((\lambda + \mu)$ t_f) | $O({1})$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Brent's algorithm | 1973 | $O((\lambda + \mu)$ t_f) | $O({1})$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Gosper's algorithm | 1978 | $O((\lambda + \mu)$ log(\lambda + \mu) t_f) | \Theta(log(\mu + \lambda)) | Exact | Deterministic | Time & Space |
Time Complexity Graph
Space Complexity Graph
Space-Time Tradeoff Improvements
References/Citation
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0304397585900441?via%3Dihub