Greatest Common Divisor: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Parameters == | == Parameters == | ||
n: number of integers | |||
== Table of Algorithms == | == Table of Algorithms == | ||
Revision as of 13:03, 15 February 2023
Description
Let $a_1, \ldots, a_n$ be given nonzero integers. Then $g$ is called the greatest common divisor (GCD) of $a_1, \ldots, a_n$ if and only if it is the largest integer that divides all $a_1, \ldots, a_n$.
Parameters
n: number of integers
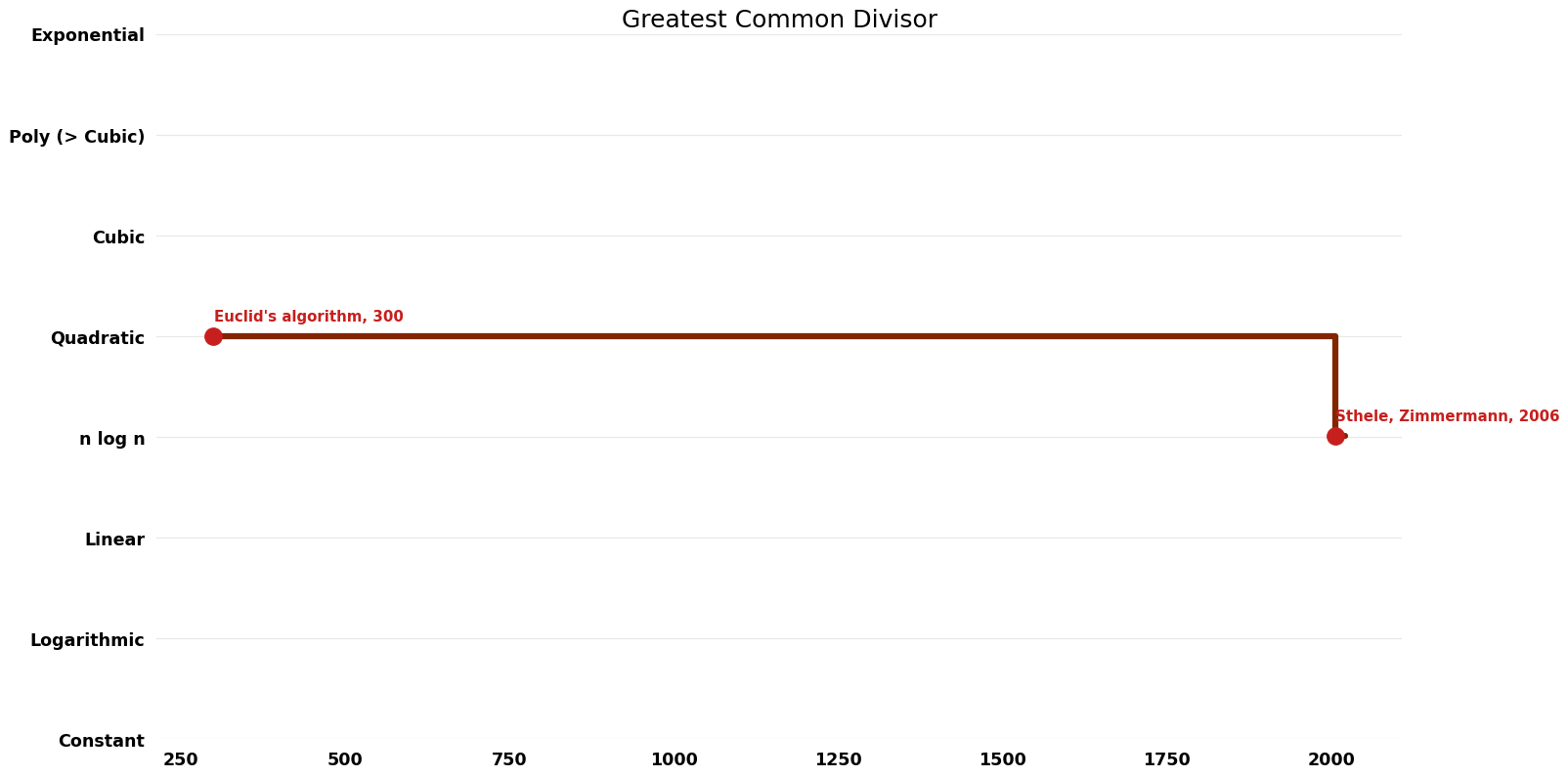
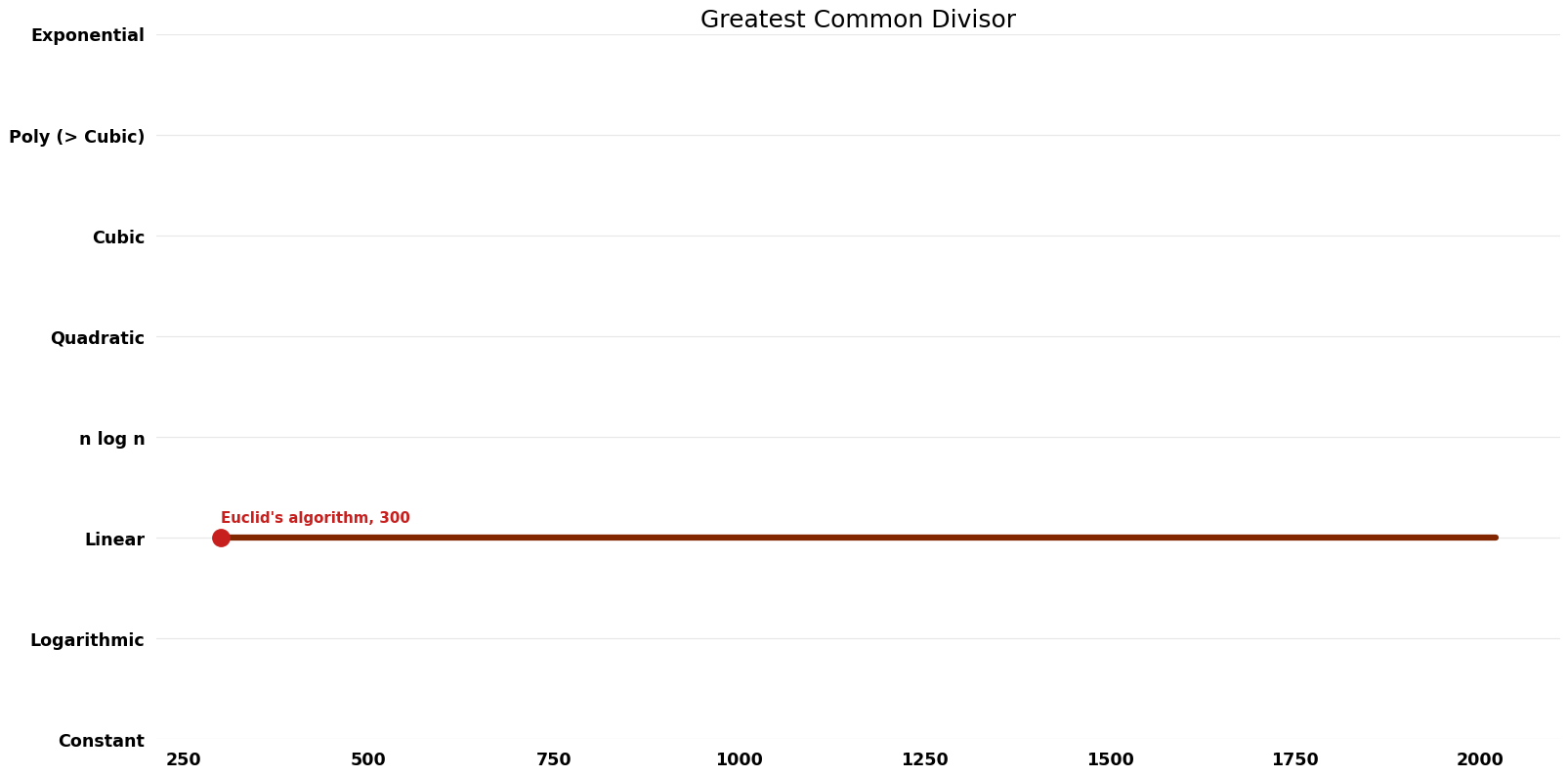
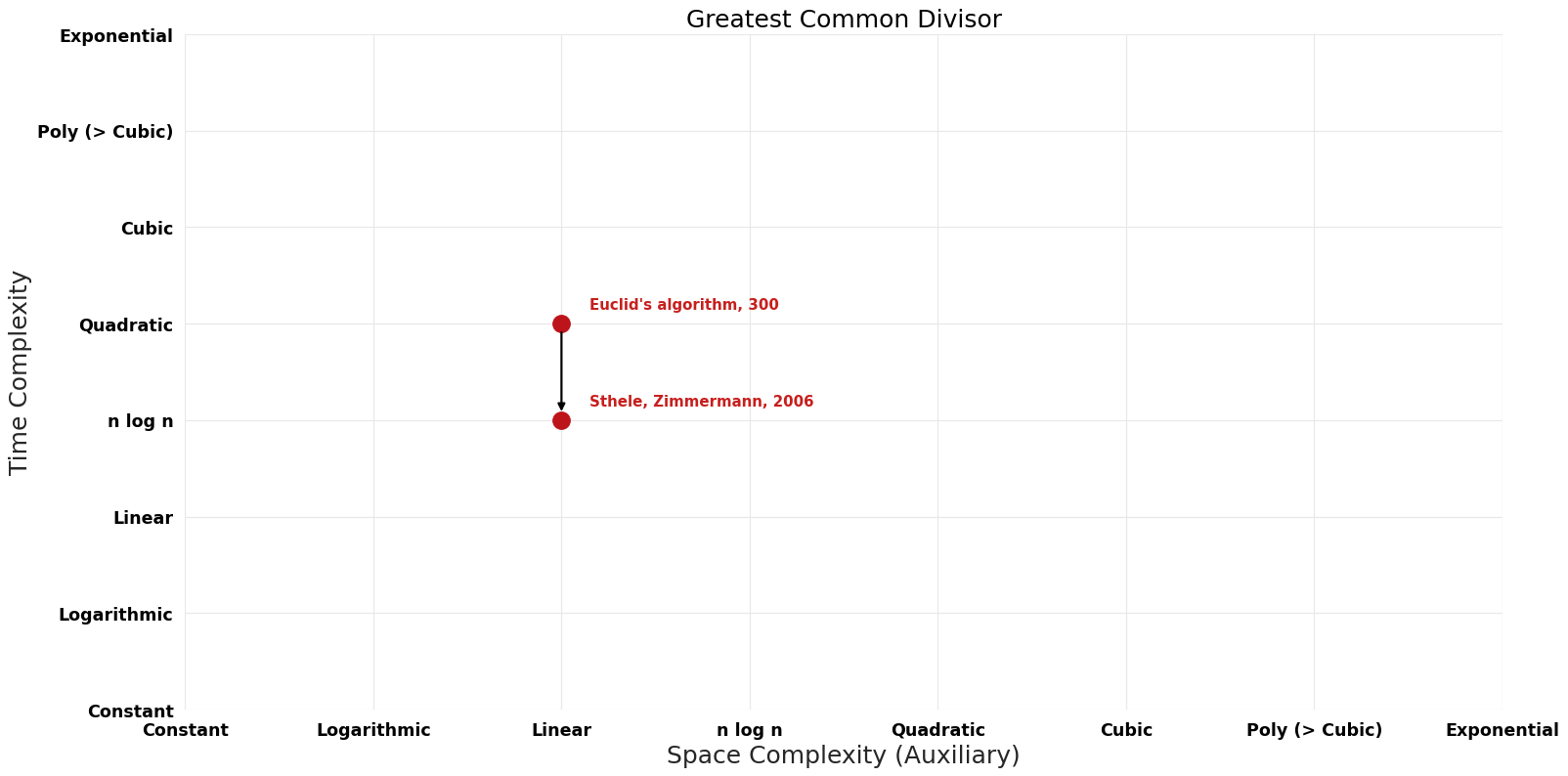
Table of Algorithms
| Name | Year | Time | Space | Approximation Factor | Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Euclid's algorithm | -300 | $O(n^{2})$ | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | |
| Lehmer's GCD algorithm | 1940 | $O(n^{2})$ | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | |
| Binary GCD algorithm | 1967 | $O(n^{2})$ | $O(n)$ | Exact | Deterministic | Time |
| Sthele, Zimmermann | 2006 | $O(n log^{2} n log log n)$ | $O(n)$?? | Exact | Deterministic | Time |